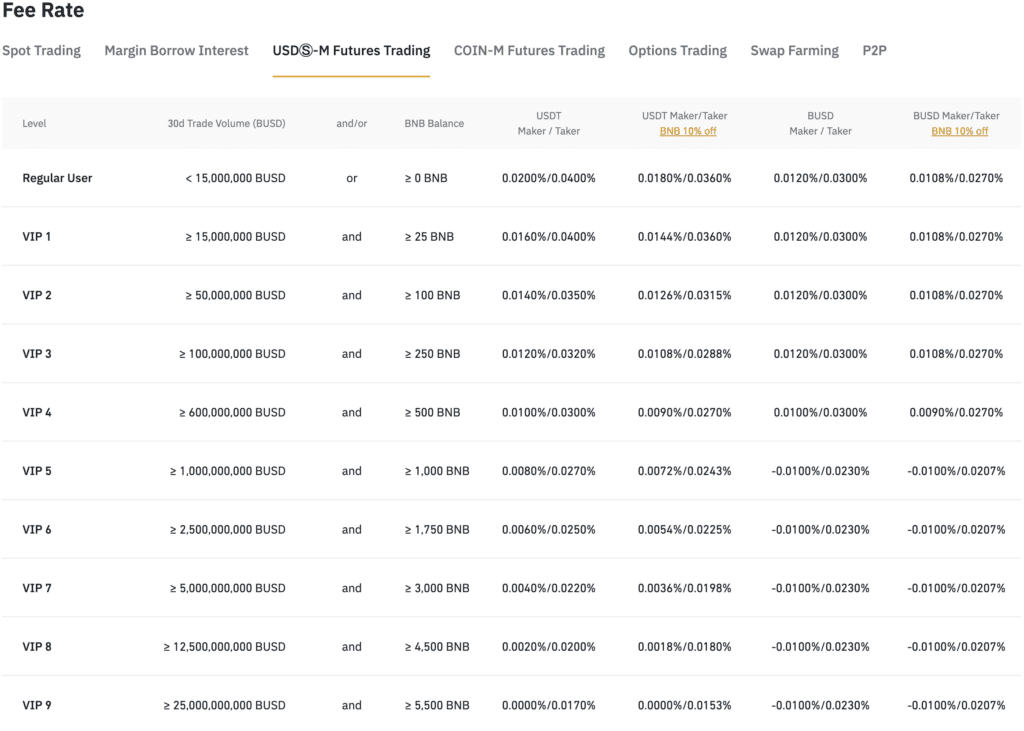
Magic Square is one of the upcoming projects that is highly anticipated by the crypto community. Imagine Apple’s App Store or Google’s Play Store integrated with blockchain technology and driven by the community. This web3 solution offers a way to simplify crypto applications hence driving adoption, creating one integrated ecosystem for all crypto apps and activity.
Magic Square’s innovation has gained the attention of many heavyweights in the crypto industry including Binance, KuCoin, and DAO Maker. All you need to know about Magic Square is in this article, made simple to understand and updated in real time.
What is Magic Square (SQR)?
Magic Square is more than a web3 app store hosting a multitude of decentralized apps (DApps) such as DeFi, NFTs, and GameFi. In fact, Magic Square has their own ecosystem which allows any user to earn crypto from using the app. We will explain this in detail later.
But first it is important to understand why a project like Magic Square might just be the missing link in driving crypto adoption.
Current Pain Points of Web3
As of today, there are nearly 6,000 active DApps running across multiple different blockchains including Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, Cardano, and more. This number does not even account for all the centralized crypto apps in the market such as Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
However, with so many crypto apps scattered on the market, there is no established platform that can host them all in one place. As a result, navigating in the crypto space can be a chaotic and cumbersome experience for both users and blockchain developers alike.
- For users, there is no all-in-one platform where they can easily discover, access, and manage vetted crypto apps.
- For developers, there is no real multi-chain service that allows them to monetize their apps and market them to users.
Magic Square’s Solution to Web3 Pain Points
Magic Square has a built-in Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) structure in which all users and developers have a say in the DApp quality control and listing process. This means that the app store is governed by the community, and they are incentivized to vet all DApps coming through the platform. Based on the principles of decentralization, this provides a secure environment for all users to engage with the listed DApps on Magic Square, as low quality projects and potential scams are filtered out, similar to how invalid Bitcoin transactions are rejected by the miners.
Magic Square is also building their own multi-chain Software Development Kit (SDK) that will help creators develop, validate, deploy, market, and monetize their DApps.
All in all, a decentralized crypto app store powered by the community as well as providing useful tools for blockchain developers could be the key to organize all DApp activities in one established platform. This would help bring order, ease, and trust to the crypto app space, which would help develop the infrastructure that powers the growth and success of the crypto industry. Now, let’s take a look at the key features of Magic Square and how their ecosystem functions as a whole.
Key Features of Magic Square
- Magic Store & Magic Spaces
Magic Store is where users can browse and download DApps, similar to Apple’s App Store or Google’s Play Store. Within Magic Store, users have a personalized dashboard called Magic Spaces where they can access all of their DApps and track their app activity in one place. By clicking on the DApp, it will be opened inside the tabs within the user’s personal space. This is a convenient feature as users do not need to switch between websites or crypto apps on their device. Additionally, Magic Spaces is fully synchronized across all devices, including desktops, web browsers, and mobile devices.
- MagicID (SSI & DIDs Technology)
Users do not have to give up control of personal information to centralized databases like Apple or Google. Thanks to MagicID which is their Self-Soverign Identity (SSI) and Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) technology, Magic Square ensures that the verifiable credentials a user has can only be shared with DApps or other users they deem trustworthy.
SSI allows users to use their digital wallet and authenticate their own identity using the credentials they have been issued. This works in conjunction with DIDs, which creates unique, private, and secure peer-to-peer connections between two connection points. Users know who they are connecting with and vice versa, and no third party can interfere in any way. The platform only collects and aggregates on-chain data about users’ app activities, which they can provide relevant and up-to-date information for users, similar to YouTube’s algorithm. Magic Square does not hold any personal data of their users.
Magic Square is developing their own SDK that allows developers to enhance their development process in various ways. Its tools are built to optimize payment system with subscription model, wallet infrastructure, trading data aggregation, on-chain data, Automated Market Making (AMM) solutions, in-app token and NFT staking, community management, and more.
Magic SDK supports common programming languages such as Java, Node JS, C++, which is easy to use for all levels of developers. In addition, the SDK is open-source, allowing every developer to add new tools that can be used by the community of developers. These tools would be vetted by certified auditors to ensure security. For more information on Magic Square’s SDK and their technical product description, their white paper is available.
Magic Square will implement cross-chain bridges using deBridge technology, allowing users and developers to transfer data and liquidity across different blockchains and protocols. This can help developers integrate their DApp from different blockchains into Magic Square. Moreover, its cross-chain functionality allows for integrated DeFi solutions in Magic Square, which we will talk about next.
Magic Square’s business model is based on revenue sharing with all pre-integrated CeDeFi solutions that will also be available to the community. These solutions include token/NFT staking, custody services, AMM pools, payment, lending, swaps, and insurance. They will be fully integrated into all DApp pages, supporting their native currencies and protocol. That way, users do not need to leave the app to access related DeFi products and services.
Moreover, any third party DeFi provider can apply to add their service in Magic Square. If they are approved by the community, their service will be added to the catalog of DeFi services in which DApp developers can use to add on their app page. For each transaction with a third party solution, Magic Square will charge payment based on transaction cost charged by the third party. This revenue will then be shared with the DApp developers, even free-to-own DApps can earn money this way.
This is how Magic Square makes money and how they fund their community reward pools to distribute SQR tokens to users, which we will cover next.
How to Earn on Magic Square?
Magic Square Token (SQR) – Utilities
The Magic Square (SQR) token is the primary unit that powers the ecosystem. Within the ecosystem, there are three types of members that play a vital role in running Magic Square: (1) users, (2) validators (3) creators. Each of them also has different ways to earn SQR tokens.
Users
Anyone who interacts with the DApp store is considered as a user. Magic Square’s core model “use-to-earn” distributes SQR tokens for all users for their in-app activities, which include downloads, comments, ratings, follows, shares, reviews, and using DApps. Individual DApps can even reward users for reviews with their own native app token, giving users the ability to earn double.
The SQR token rewards are based on the personal ranking of the user which is called “Magic Karma.” All in-app activities are summarized and quantified on a daily basis in the Magic Karma score. The higher the user’s score, the more rewards they can earn. As cited in their lite paper, users can “earn SQR tokens without investing their money, just their time.”
Users can also stake SQR tokens to unlock different levels of Packages which grant them additional perks. “Base Package” requires 150 staked SQR for unlimited DApp downloads. “Pro Package” requires 500 staked SQR for daily rewards and referral bonuses. Lastly, “Influencer Package” requires 1000 staked SQR and a high Karma score to unlock daily reward boosts and access to Magic Square events and exclusive contests etc.
Validators
To fill the role of Apple/Google engineers, Magic Square has validators to determine which DApps to feature in the store. There are three types of validators: (1) qualified validators, (2) nominees, (3) standard validators. Although all community members are eligible for these roles, there are certain conditions that must be met.
To become a qualified validator, you must stake 5,000 SQR tokens, and pass a qualification test to demonstrate your level of knowledge and competency. Qualified validators can also transfer validating rights to nominees. However, nominees must also pass the qualification test, but do not need to stake SQR tokens. On the other hand, any user can register as a standard validator without passing the qualification test or stake SQR tokens.
80% of the DApp creator’s validator fee is rewarded to qualified validators, which a portion of it is also shared with the nominees. The remaining 20% is rewarded to standard validators.
Creators
All DApp developers and their project team are considered as creators. For creators to have their DApp listed on the Magic Store, they would have to send 10,000 SQR via smart contract, where 35% is paid to validators, 15% is paid to Magic Square, and 50% is staked for the period the DApp is listed in the Magic Store.
From the list of pre-integrated DeFi services, creators can choose to add them in their DApp page, allowing them to manage their liquidity through in-store interaction. With a higher rate of DeFi adoption by users, creators can efficiently engage with their target audience and increase market penetration.
Furthermore, each newly listed DApp can apply for a grant of up to 200,000 SQR tokens to be used by the creators to build and improve their product. However, creators must first stake the number of SQR tokens to match the amount they are requesting, for 12 months. The grant would be decided through voting processes by the validators.
Who is the Team behind Magic Square (SQR)?
Magic Square is co-founded by Andrey Nayman (CEO) and Benjamin Vodovozov (CMO), both who are seasoned entrepreneurs and mathematicians who have decades of experience in quantitative analysis and performance marketing.
The team consists of a first-class group of industry professionals, blockchain veterans, software developers, and crypto enthusiasts. Their goal is to gradually influence a widespread organic shift to the web3 space, and they aim to achieve that by developing infrastructures that power the growth of the crypto app ecosystem.
What’s Happening with Magic Square (SQR)?
In July, Magic Square concluded a $3 million seed round investments with an evaluation of $30 million, led by Binance Labs and Republic Capital. Mia Mai, Investment Director at Binance Labs, commented that they see potential in Magic Square, especially in their user-friendly designs and business model as a Web3 DApp store. They believe that the product suites of Magic Square can potentially be the driving force of Web3 ecosystem mass adoption and implementation.
Other crypto industry heavyweights have also become strategic partners with Magic Square, including KuCoin Labs, GSR, DAO Maker, IQ Protocol, Gravity Ventures, Alpha Grep, and other angel investors.
Several major web3 brands have integrated with Magic Sqare including Chainlink, KyberSwap, Banxa, and deBridge.
Key Takeaway
Magic Square is definitely bringing something new and innovative to the crypto space. Its product could essentially organize all DApp activities that are scattered throughout the market, making it easily accessible to crypto users and newcomers. Magic Square published their roadmap, stating that their token will be released in Q1 2023. We are now witnessing many crypto heavyweights such as Binance recognizing the potential of Magic Square and their ability to drive mass adoption through simplicity.