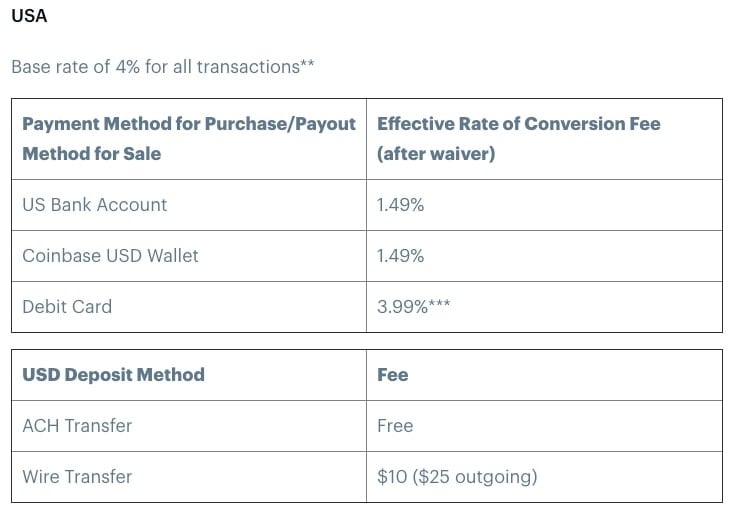
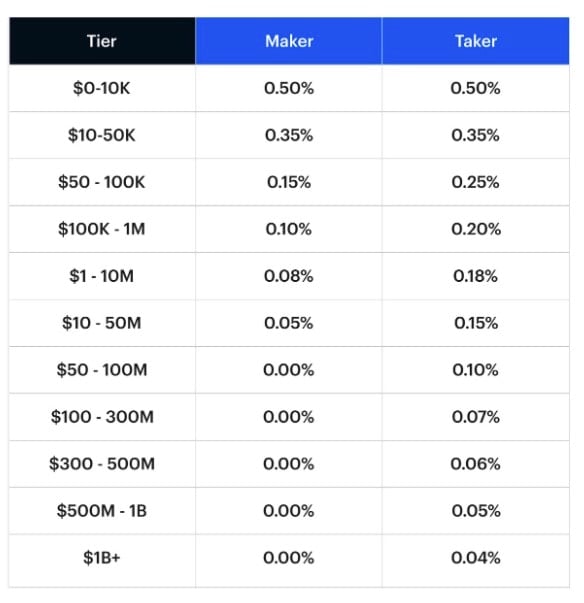
Kusama ($KSM) calls itself “Polkadot’s wild cousin”. Yet, is an initiative that seeks to solve the Polkadot ecosystem’s concerns of coding vulnerabilities. Going beyond the usual testnet, Kusama deployed on its platform a network focused on research and development with real costs to its community and developers. This makes it more mainnet-like, without having to actually put new developments up on the main Polkadot platform.
Background
Dr. Gavin Wood founded Kusama with a goal of supporting the Polkadot ($DOT) network via building a parallel blockchain that allows experimentation and development with very realistic conditions. With that in mind, Dr. Wood thought of having a “canary network” that functions as a warning and early problem detection protocol that can reveal the weaknesses of the Polkadot code base.
With Kusama, new features that are planned for implementation on the main Polkadot chain can be tested. The difference between Kusama and all other testnets is that the decisions made in the platform have actual economic implications. Testnets only provide playground tokens that bear no actual value.
What is Kusama?
Kusama is Polkadot’s canary network, which means that it is an experimental community research and development protocol. Its main purpose is to help developers test and deploy parachains on the Polkadot project, or experiment on its governance and staking functions with real economic conditions.
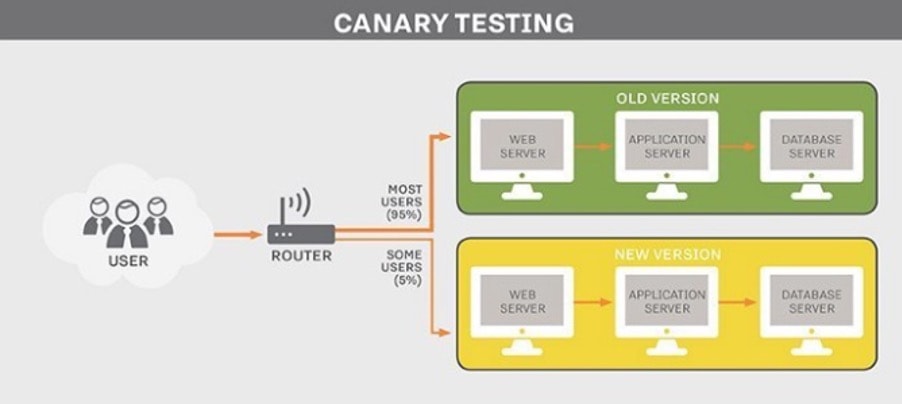
Canary testing is important as the developers behind both chains hypothesize that it is the best way to completely understand the critical risks that lie in Polkadot’s development.
As an unrefined version of Polkadot, Kusama functions as an independent decentralized main network. It will continually function as long as the community allows it to since decentralized systems inherently have no kill-switches. It could possibly become a para relay chain to Polkadot, however, it is never intended to merge with Polkadot’s chain itself.
Kusama Token ($KSM)
Kusama’s native token is the KSM, which holders can use to stake, become a validator or nominate one, and vote on its governance mechanism, among others. Furthermore, it is the token that powers most of the mechanisms in the Kusama network.
Investors who purchased DOT during Polkadot’s ICO are qualified to receive an equivalent amount of KSM on the Kusama Network.
Consensus Protocol: Nominated Proof-of-Stake
Kusama follows the Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) consensus model where validators are elected based on their stakes and the stakes of those who are voting for them. As much as possible, the platform balances the weight between validators every election.
In Polkadot, the election of validators focuses on the balance between these three metrics (Phragmen’s algorithm):
- The total amount staked by the nominee and their nominators
- The stake behind the minimally staked validator
- The variance of the stake in a set.
Validators
To become a validator, users are required to stake KSM first. Once users already have the minimum amount of tokens needed to become candidates for a validator set, they are elected based on the Phragmen’s algorithm.
There are currently over 130 validators on Kusama.
Parachains
Parachains are application-specific data structures secured by validators on the Polkadot Relay Chain and run in parallel with the Polkadot network. This allows them to process transactions with the speed and scalability of the Polkadot blockchain.
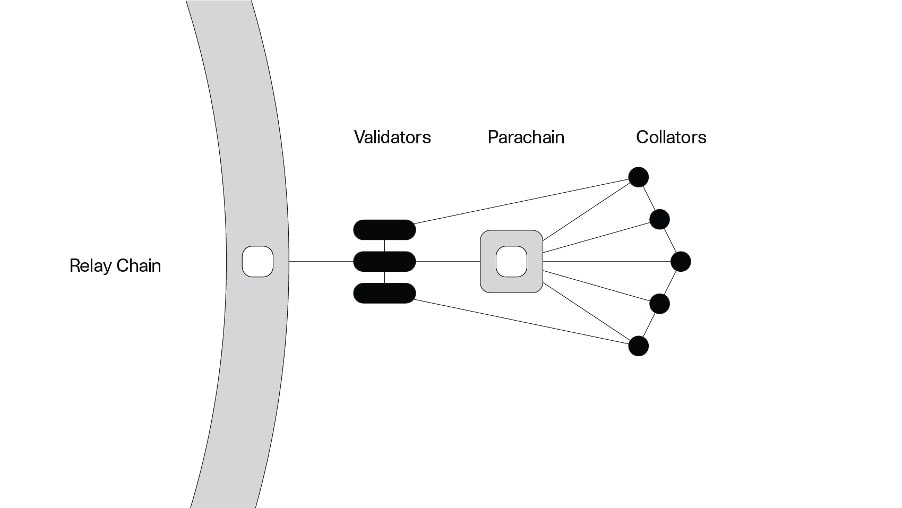
Collators, on the other hand, are tasked to maintain the whole parachain. Collator nodes keep every data concerning the parachain and create new block candidates for the verification and recording of validators.
Parachains can have an independent economy from the Polkadot network and their own native token.
Governance
Before every protocol update or revision is made, they are voted upon by the network composed of token holders and Kusama’s council. Through innovations such as on-chain voting systems and stake-weighted decision making, Kusama has enabled a community-driven governance model.
The governance function follows the following procedures:
Proposing Referenda: Each referendum contains a specific proposal that serves as a privileged function call. Included in the referenda is the period designated for the voting process. They can be submitted by Polkadot (DOT) token holders and the council, or taken from prior referenda or recommendations by Kusama’s Technical Committee after the approval of its Council.
Voting for a proposal: There are only two options when voting, either “aye” or “nay.” If proposals receive a majority, they can be carried out for implementation. Before the enactment of a proposal, however, users are required to lock their tokens until the whole enactment delay has lapsed. The purpose of this parameter is to ensure that a proposal has met the minimum economic buy-in and discourage vote selling.
Tallying: There are three scenarios whenever the network votes on specific proposals. Since each proposal is distinguished on whether they are from the public or the council, the votes also differ in bias.

For every proposal, the number of “aye” and “nay” votes are accounted for as the turnout, or the total number of voting tokens, are factored in.
In a positive turnout bias (if the voter turnout is low), more votes in favor of the proposal are required. In a negative turnout bias, it requires more votes against the proposal. And for Council proposals, only a simple majority is necessary.
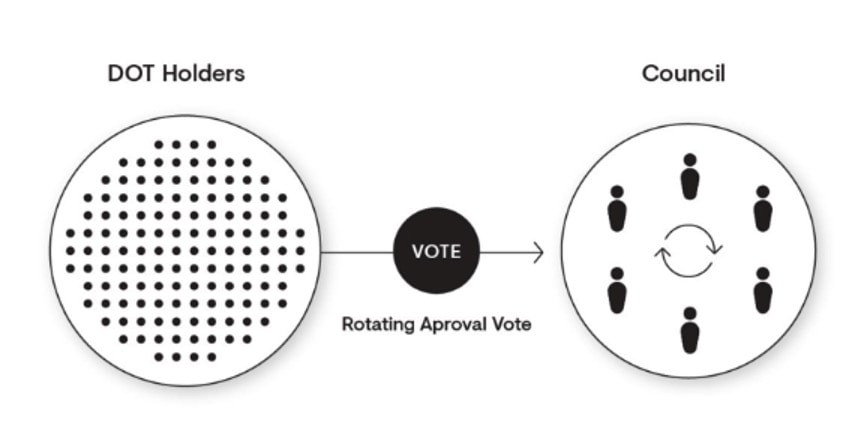
Kusama Council
While there are active stakers, there are also passive stakeholders in the Polkadot and Kusama ecosystem. Through an on-chain entity comprising of 17 seats, the Council decides on three main tasks of governance. These include proposals of referenda, striking out clearly dangerous referenda, and electing members of the network’s technical committee.
Community on Kusama
Kusama has deployed the Society module, an economic game that seeks to reward users for participating and maintaining a membership society. Rewards, however, are given maturity periods. This means that the user cannot instantly get their incentives until the maturity period of their entitlements has already lapsed.
Societies can punish members by slashing their incentives if they are not being collected. There are many other violations, such as not participating in voting calls, among others.
By a strike system, members who have committed a number of punishable actions exceeding the limits decided upon can be booted out of the society.
As of now, Kusama only has one society organized on top of its platform. In the future upgrades though, they might add more.
Conclusion
The growth of the DeFi space is dependent on the participation of both its developers and the community behind them. Projects that empower developers to test out new features before they are actually implemented on main channels are important, especially if the security and reliability of a particular network are at stake.
A project like Kusama enables developers and their community to play around the Polkadot platform while making sure that each feature they are planning to deploy is not only audited but also tested realistically.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
- MetaMask Guide: How to set up an account? PLUS tips and hacks for advanced users
- Uniswap review and tutorial: Beginners guide and advanced tips and tricks
- Serum DEX guide and review
- SushiSwap ($SUSHI) explained
- 1inch Exchange, Mooniswap and Chi GasToken: The ultimate review and guide
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.