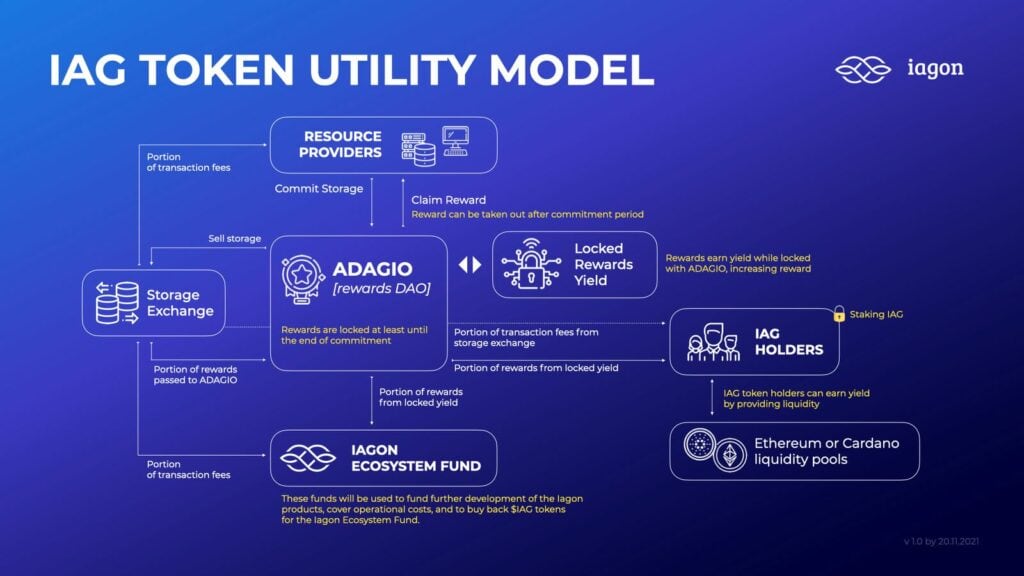
One of the core problems with the Ethereum network today is scalability. As more and more decentralized apps (dApps) are built on the network, the number of users and transactions increases. This has slowed down the speed of transactions and driven up the cost of using the network, creating the need for scaling solutions.
At its full capacity, the Ethereum network is only able to process 15 transactions per second. To put Ethereum’s scaling limits into perspective, consider that Visa handles around 1,700 transactions per second on average. Therefore, increasing the network capacity in terms of speed and throughput is fundamental to the meaningful and mass adoption of Ethereum.
There are multiple solutions being researched, tested and implemented that take different approaches to achieve similar goals. Two solutions that we will explore in this article are known as sidechains and optimistic rollups.
Check out our explainer video on layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum, Boba, Optimism, and Ethereum 2.0
What is Layer 2 and How Does it Work?
The Ethereum main chain is known as Layer 1. Layer 1 applications and smart contracts interact directly with the native chain. Layer 2 refers to a series of different protocols that facilitate the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on top of the core Ethereum blockchain.
Operating on Layer 2 frees up Layer 1 by taking transactions off the main chain, offloading it to Layer 2, enabling them to interact, and then recording the remainder of the whole transactions back to Layer 1. Due to transactions being processed off-chain on Layer 2, Ethereum benefits from higher transaction processing capacity, faster confirmation times, and lower gas fees.
In fact, many believe that Layer 2 solutions will be how Ethereum wins over mainstream users. It is estimated that 2,000 – 4,000 transactions per second can be processed in Layer 2, which is already in line with Visa’s processing capabilities. By combining the scaling of Layer 1 with Ethereum 2.0 and Layer 2, Ethereum is set to obtain a powerful economic bandwidth.
Sidechains: Polygon Network
Sidechains are a Layer 2 solution utilizing separate blockchains that run in parallel to the Ethereum main chain but operate independently, hence increasing its scalability.
Polygon is the most popular sidechain that aims to scale Ethereum by building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Polygon operates on its own consensus mechanism and also has its own native token known as $MATIC.
Because sidechains run on a separate blockchain, they do not inherit the security of Layer 1. If a sidechain is hacked or compromised, the damage will be contained within that chain and will not affect the main chain. Conversely, should the main chain become compromised, the sidechain can still operate.
Sidechains also provide room for a lot of flexibility, allowing developers to experiment with new features or software updates before pushing them onto the main chain.
Rollups Explained: Optimistic Rollups & Zero Knowledge Rollups
Rollups are another Layer 2 solution intended to solve Ethereum’s scalability and complement the network. Rollups interact with the main chain, therefore inheriting Layer 1’s security features as well as its secure consensus mechanism. The term ‘rollup’ refers to the way that the chain bundles many transactions to be submitted to the main chain.
Because rollups use smart contracts that reside within Ethereum, they do not require a native token like Polygon, but instead use $ETH as their currency. Rollups seem to be the most sound scaling solution for Ethereum as it does not compromise the security and sovereignty of Layer 1.
There are basically two types of rollups: Optimistic Rollups and Zero Knowledge Rollups (ZK Rollups). Both aim to scale Ethereum by processing transactions on Layer 2 before submitting the results back to Ethereum. However, the difference is in how they validate transactions.
In simple terms, Optimistic Rollups assume that transactions are valid — hence an optimistic outlook. However, it also allows what are called “watchers” to call out fraudulent transactions since blockchain is transparent and public. If a watcher proves instances of fraud, the transaction is reverted, the bad actor penalized, and the watcher rewarded to incentivize them.
On the other hand, Zero Knowledge Rollups attempt to prove that transactions are valid. They do so by submitting validity proof to an Ethereum smart contract along with the bundled transactions.
Optimistic Rollups are currently the more popular option, so let us look at some projects that have adopted this mechanism. These projects are Arbitrum, Boba, and Optimism.
Optimistic Rollups: Arbitrum, Boba & Optimism
Arbitrum, Boba and Optimism are 3 projects which have the same goals of scaling Ethereum and reducing gas fees. All of these Layer 2 projects are competing with one another to be the best network. Therefore, each project offers different features to stand out from the others.
- Arbitrum describes itself as a Layer 2 solution designed to improve the capabilities of Ethereum smart contracts — boosting their speed and scalability while adding additional privacy features to boot. Arbitrum is, according to the team, around 90-95% cheaper than Ethereum. And with their Nitro being launched soon, they expect costs to be cut even further.
- Optimism is an EVM-compatible Optimistic Rollup chain designed to be fast, simple, and secure. Optimism pledges to uphold the values of Ethereum by producing infrastructure that promotes the growth and sustainability of public goods.
- Boba Network is a next-generation Layer 2 scaling solution that reduces gas fees, improves transaction throughput, and extends the capabilities of smart contracts, shrinking the Optimistic Rollup exit period from seven days to only a few minutes, while giving liquidity pools (LPs) incentivized yield farming opportunities.
Arbitrum’s fraud proofs seek to find the particular point of disagreement over transaction history. In contrast, Optimism’s tech looks at fraud a bit more holistically. And this means that Arbitrum has a higher transaction capacity equating to higher performance.
Optimistic Rollups have a time period in which users can dispute transactions and call fraud. Both Arbitrum and Optimism allow one week for that dispute period, which means that transactions in a bundle under suspicion can be held in limbo for one week before they are verified and released. This is where Boba comes in as a serious player.
Instead of having funds locked for several days, Boba’s solution brings the dispute period down to only a few minutes. It also provides incentivized yield farming opportunities, both serving as very attractive features in comparison to its competitors.
Will Ethereum 2.0 Make Layer 2 Solutions Irrelevant?
Ethereum 2.0 is regarded as the long-term solution that can bring speed, efficiency, and scalability to the Ethereum network. The long awaited upgrade will move the network from a Proof-of-Work consensus to a Proof-of-Stake consensus, a much more energy efficient method of maintaining the network that uses validators instead of miners.
Ethereum 2.0 is currently slowly being released in different phases and will ultimately speed up transactions as well as drastically reduce the cost of gas fees. That brings up the question: Will Ethereum 2.0 make all these Layer 2 solutions irrelevant?
While there are many different opinions and discussions surrounding this topic, however, we think that all of these solutions can coexist and benefit the network as well as its economy.
This is because despite the upgrade, Ethereum 2.0 may still not be able to handle the amount of transactions per second required for widespread adoption. The impressive capabilities of Layer 2 solutions could eradicate Ethereum’s scalability issues for good, allowing the network to improve other aspects and prevent congestion on the main chain.
Final Thoughts: Why Are So Many Solutions Needed?
There is no debate that Ethereum has a stronghold over developer mindshare. It is the first network that enabled developers to build truly unstoppable decentralized applications with global distribution from day one. But competition is coming fast, and as it stands today, Ethereum will not be able to handle the scale necessary for millions of users. If the network wants to retain the same level of decentralization, it will have to look for new ways to structure use around the main blockchain.
As such, there are currently several Layer 2 solutions that aim to resolve Ethereum’s scaling issues. There are also some hybrid solutions which seek to improve the network’s scalability by combining the technologies. But is there really a need for so many solutions?
We say yes, because multiple solutions can help reduce the overall traffic on any one part of the network, and also prevent single points of failure. The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Different solutions can exist and work in harmony, allowing for an exponential effect on future transaction speed and throughput. Furthermore, not all solutions require utilizing the Ethereum consensus algorithm directly, and alternatives can offer benefits that would otherwise be difficult to achieve.
If Ethereum achieves its full potential of becoming a global trust layer, it is likely that these solutions and more will be required to scale the network in combination with Ethereum 2.0. In the future, the Ethereum ecosystem could see significant change as new projects assess the benefits and drawbacks of running on Layer 2.
If all of these solutions can come together in harmony, Ethereum will achieve a blockchain system that can match the speed and scale of programmatic advertising – one that can be used by industries with high data processing needs as well as users worldwide.
Sources:
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/
https://hackernoon.com/ethereums-layer-2-the-story-so-far-and-what-to-expect-next-kn41342c
https://dappradar.com/blog/ethereum-rollups-a-simple-explanation