The Ethereum network has immensely pushed the boundaries of blockchain technology more than Bitcoin ever had, especially in the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector, where hundreds of different projects have been able to leverage the flexibility and effectiveness of the host blockchain.
Unfortunately, the slow transaction speeds and high costs are significantly limiting the performance of Ethereum-based projects to the point that some of them are migrating to alternative chains like Solana and Binance Smart Chain. Yet the vast majority of applications still hold on to Ethereum, waiting for Ethereum 2.0 to fully scale the network.
Ethereum is in dire need of a scaling solution that can speed up the blockchain’s throughput. Thankfully, Polygon is working on one of such solutions that would see the load on the Ethereum blockchain eased on parallel child chains.
Background
Polygon started out as Matic Network, a blockchain solution intended to speed up blockchain transactions and make them more accessible to the general public. Later on, the company refocused its objectives on the Ethereum network to furnish it with layer two scaling solutions. The name Polygon came along with the branding.
The startup was founded by four Indian technologists, Jaynti Kanani, Anurag Arjun, and Sandeep Nailwal, who had a similar vision of a future where machines and humans interacted freely. The three entrepreneurs agreed that blockchain technology is a vital tool for achieving such a society.
The trio was later joined by a Serbian tech maximalist and Ethereum enthusiast, Mihailo Bjelic. In a seed round announced on the 1st of August, 2019, Polygon received funding from MiH ventures through Crunchbase. Version 1 of Polygon’s SDK was scheduled to be released in March of 2021.
What is Polygon ($MATIC)?
Polygon is a framework that allows Ethereum-based applications to bypass the low throughput, high gas fees, and poor interface of Ethereum while still enjoying its support
Polygon’s main component is its software development kit (SDK). The SDK is a flexible structure that allows projects to develop different sidechains that suit their needs. Necessary support is provided so that the alternate chains can interact effectively with Ethereum’s main chain.
By arming developers with flexible and easy-to-use tools, Polygon accelerates the transformation of Ethereum into a multi-chain ecosystem. Its users would be able to create Optimistic rollup chains, ZK rollup chains, and other types of sidechains.
But beyond being a mere framework, the Polygon platform is focused on connecting blockchains with one another, as well as the Ethereum blockchain itself.
Advantages of Polygon
The major benefit of Polygon is scalability, which the crypto space is in dire need of today considering that it takes forever for transactions to be verified on the Ethereum network, especially if you try to decrease the gas fees. Dapp developers have to pay so much in gas fees that it curtails their development and affects their offering to users.
And this is the pain point that Polygon aims to ease, and they are on their way to scale the Ethereum network.
Polygon for Developers
Developers can build a network of scalable side chains to the Ethereum blockchain through Polygon; one with independent consensus algorithms on a more developer-friendly, Web Assembly (WASM) environment.
Developers would be encouraged to build more and advance the general direction of the crypto industry, especially the DeFi sector. Polygon’s SDK does not require developers to have blockchain expertise. In fact, knowledge of these protocols is unnecessary in building from its SDK.
Users would also benefit tremendously with more easy-to-use interfaces, near-instantaneous transactions, and low costs. If well-executed, this will likely propel the growth of Ethereum dapps to astronomical levels and will push the boundaries of crypto to include the masses outside the industry.
Support, Flexibility, and Security
Polygon permits incredible flexibility for the development of chains.
Its modular nature allows developers to assemble products at unrivalled speeds. The easy assembly will also accelerate dapp development, effectively shortening the interval between the conception and deployment of blockchain products.
Support would also be provided for easy interaction with users, as well as external systems. Token exchange, contract calls, and communication with oracles are also supported on Polygon. Furthermore, the products would be easily upgradeable.
All these and more will be possible on Polygon without compromising on security. In fact, developers would be free to choose their approach to secure their platforms, using the modular “security as a service” feature on the Polygon framework.
Above all, all products developed on Polygon would be compatible with Ethereum.
Polygon Chains
During the days of Polygon’s Matic network, an Ethereum sidechain that uses the Plasma framework was the landmark of its offering. The Plasma framework allowed sidechains to run independently, only interacting with the main blockchain when it was necessary.
Polygon’s new platform sees it advance with the demands of the market by offering different chain networks that are attuned to Ethereum’s blockchain. And these are: stand-alone chains and secured chains.
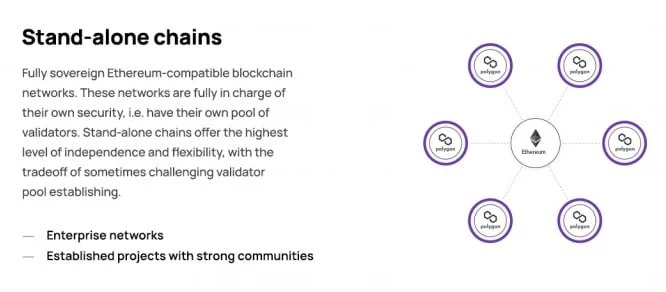
Stand-alone Chains
Stand-alone chains have security autonomy, with each chain being responsible for its own security. Such chains have the freedom to choose their own validation methods. They can establish a personal pool of validators who ensure the authenticity of transactions directly on the blockchain.
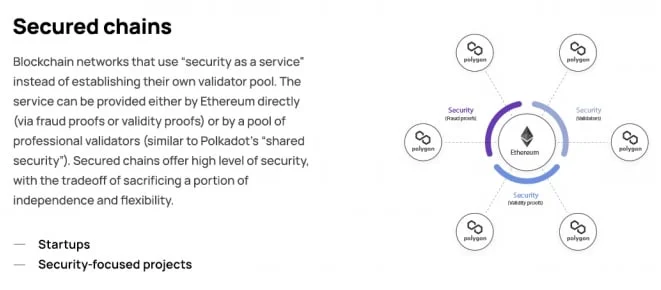
Secured Chains
On the other hand, secured chains involve outsourcing the platform’s security to a third party. The third-party can be Ethereum itself, with its fraud-proof and validity proof pools. There are other independent, professional pools of validators that offer security as a service as well.
Overall, secured chains often enjoy more reliable and tighter security even if they might have to sacrifice some independence.
MATIC token
MATIC is the only native token of Polygon, it is used to pay transaction fees and participate in Polygon’s proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
Conclusion
Polygon’s vision is to launch whole blockchains that are scalable, secure, and have amazing interfaces, allowing decentralized applications to have an alternative platform to carry out transactions while enjoying the security and support of the Ethereum network.
Meanwhile, the Ethereum dev community is also continuously working on the Ethereum 2.0 project (Serenity), which seeks to ultimately scale its blockchain to unimaginable capacities even beyond Visa and Mastercard.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

