Litentry ($LIT) is a decentralized cross-chain identity aggregator, built on Substrate, that features an identity matching and identity staking mechanism.
In today’s world, personal data and identity are everything. Some companies in the conventional world make millions by selling user data. In the decentralized world, blockchain-based firms make losses.
For example, one user can create multiple accounts to take advantage of free airdropped tokens. Also, platforms powering decentralized finance (DeFi) have no way of tracking users’ credit history, making them charge higher collateral when issuing loans.
Fortunately, there’s a new way to keep track of identities in the distributed ecosystem securely. Powered by Litentry, we can see blockchain-focused platforms do more than just power token swaps. It’s now possible to scan through user’s deposit and withdrawal actions on Uniswap. Furthermore, a user’s activity can also be assessed on a community-governed blockchain.
Since the platform is so diverse, below, we look at the major highlights.
Background
Litentry is developed by a team of blockchain professionals based in Germany. Its founder was among the early contributors of Parity, a decentralized network. Notably, the project engineering team’s background is rooted in Ethereum.
The protocol is funded through a Web3 Foundation grant. On its Github page, the project lists eight team members with organization permission.
What is Litentry?
The project focuses on decentralized identity (DID), allowing user identities to be linked to multiple distributed protocols. Litentry acts as a DID aggregator where it collects, indexes, and distributes DIDs to blockchains.
More importantly, it performs all these activities in a decentralized and verifiable way. Notably, built on the Substrate network, the platform works towards the greater goal of eradicating identity redundancy in the Web3-powered application ecosystem.
The problem
In the current internet world, third parties take control of storing user passwords and data pertaining to their online activity. Unfortunately, internet users are coerced into accepting unfavorable terms and conditions, consequently lessening the grip on their personal data.
Litentry brings the change by returning the control of user data to the users by powering a user-focused internet using blockchain technology. As such, the revenue emanating from using users’ data gets the users to share in the profits. Before Litentry, these profits went to third parties managing the user data.
Key Features of the Litentry platform
Apart from using decentralized ledger technology (DLT), the platform has other critical features that help it bring the much-needed revolution to the blockchain sector. Key among them include:
- Identity management – The platform is all about identities, and their management sits at the protocol’s core. This feature powers anonymous and independent identities emanating from applications and or services used by the user.
- Distributed storage – After collecting the data, the protocol stores them in a decentralized manner to enhance access from all corners of the distributed world.
- Identity staking – This is a unique feature. Just like staking tokens and earning rewards, Litentry enables users to stake their identities and be rewarded.
- Decentralized contributors – Instead of creating multiple accounts to use different platforms or services, the project allows users to use one identity to interact with various services anonymously. Interestingly, the user doesn’t have to provide passwords or any other registration details.
Litentry Architecture
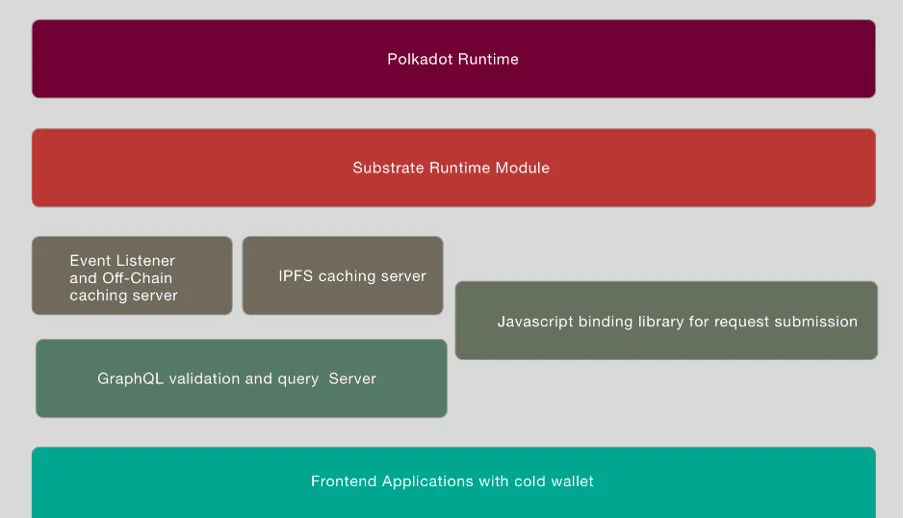
To bring all the above features to life, the protocol uses a layered architecture. On the top layer is the Litentry Runtime, which sits on Substrate. The Runtime layer is a Parachain of Polkadot and employs offline workers when generating identities.
The second layer is the User Side. Here, users flex their muscles when it comes to data under their control. Note that user data that comes from applications are anonymous, stored in a decentralized way, and cryptographically-separated.
On the Litentry Authenticator layer, we have the mobile data hub. The hub can be used to manage a user’s different identities. Additionally, the hub can be connected to various IoT devices that the user wants.
Next is the Litentry SDK enabling developers to fire up their creative juices to create completely decentralized applications and/or services. In addition, the Litentry IPFS data center offers users a chance to check the data attached to their identities.
The middleware layer comprises services such as off-chain catching and query servers. It is also made up of a client-side SDK library that helps connect front-end apps with decentralized networks.
Litentry Tokenomics
The incentive mechanism on the Litentry platform takes into account different participants such as an identity staker, validator, external storage, node, and data buyer.
- Identity staker — This is the person who has an identity record and has a stake in the identities pool.
- Identity validator — An identity staker becomes a validator of new blocks when their identity has been confirmed.
- Storage — Stores all data about an identity in a decentralized manner.
- Node — The node is a critical component of the Litentry platform. Its work is to perform functions such as invoking off-chain workers to validate identity correctness and connecting with external decentralized storages.
- Data buyer — This is any entity on the blockchain that requests identity validation.
- Data generator — These are entities generating data and can include applications, users, or services offering migration services.
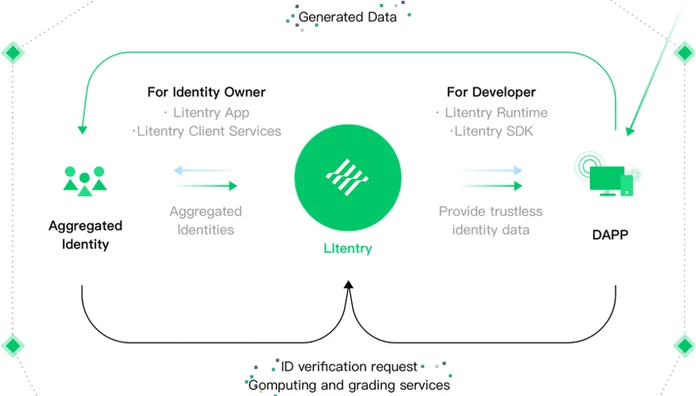
Litentry Native Token (LIT)
Litentry’s base asset is called LIT. The network uses the asset to reward identity stakers in the identities pool. Two types of rewards the stakers get are the block reward and the matching fee.
Apart from stakers, validators are motivated to truthfully verify the correctness of data. On the other hand, data generators enjoy benefits from the Litentry Foundation in the form of grants.
External storage operators earn a section of the fee paid by users interfacing with the service. Others who are incentivized using LIT tokens are nodes.
Those who pay using LIT tokens include identity buyers. Observe that these entities only have access to the winning identity or identities during an identity matching process.
Conclusion
The identity problem is two-pronged; users can create multiple entities to defraud a company. On the other hand, malicious actors aggregate user data and sell it to the highest bidder without profiting the real data owners.
Fortunately, Litentry uses a layered approach to comprehensively tackle the problem to the benefit of both identity owners and decentralized platforms. Here’s to another promising project with a unique approach to solving some of the most crucial problems that often go overlooked.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

