Kyber Network is an Ethereum-based protocol that can access any ERC-20 tokens, bridging liquidity pools and enabling tokens swaps all under a single platform. It is a tool for payments, financial applications, and liquidity providers.
Background
Loi Luu, CEO of Kyber Network, conceptualized the platform out of the need to link liquidity pools across different blockchains to facilitate cost-efficient trading. The team also decided to do away with the centralized model for creating new exchanges because of their dark history with hacking and fraud, with Mt. Gox being a notorious example.
With decentralised finance (DeFi) leading the crypto space, it was also ideal for the team to create an ecosystem born out of the same model. Through DeFi, Kyber can connect liquidity pools with one another to create a cost-efficient exchange that can accommodate smart contract innovations as well.
What is Kyber Network?
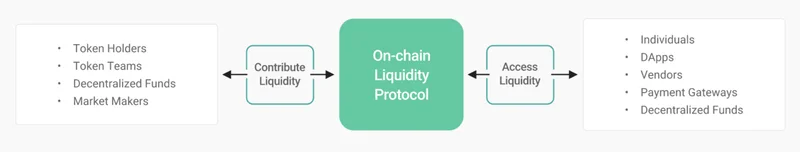
Kyber Network is a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange (DEX) powered by smart contracts. It is designed to support liquidity pools from different blockchains for market-making, allowing traders to get the best rates out of their transactions. The DEX currently lists 81 cryptocurrencies and 82 trading pairs.
Kyber’s main goal is to aggregate different liquidity providers in a single, unified ecosystem where users can conduct their trades conveniently. Since the network is decentralized, even users can provide liquidity by staking in Kyber’s partner pools.
The architecture of Kyber allows for instant transaction settlement while offering a wide array of use cases, such as building new financial services and operating crypto-based payment systems. Through its flagship models like Peace Relay and the Waterloo Relay Bridge, Kyber connects multiple blockchains together in creating a liquidity network that can be deployed in almost every other protocol.
Included in Kyber’s thrust is to create a community-guided network through governance tokens. Like other decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO), users can help maintain the network by voting on important protocol updates, parameters, and implementation features.
Features of the Kyber Network
The design of the network is mostly facilitated by smart contracts that can work cross-chain. As mentioned, the end goal is to make a market that offers the best token exchange rates for traders and the best returns for liquidity providers.
- Aggregated Liquidity Pool: The protocol can put together different liquidity sources into a single pool to reduce the risk of huge spreads and help traders get the best value out of their transactions. Users do not have to broadcast multiple trade calls in order to find the best prices themselves.
- Diversified Liquidity Source: Since the system of the network is designed for cross-chain functionality, any other liquidity network can connect with Kyber to join the platform.
- Permissionless: Unlike centralized exchanges, the network is not governed by a single company. This gives more freedom for liquidity providers or developers to work on their own strategies without the risk of an entity monopolizing control over the exchange platform.
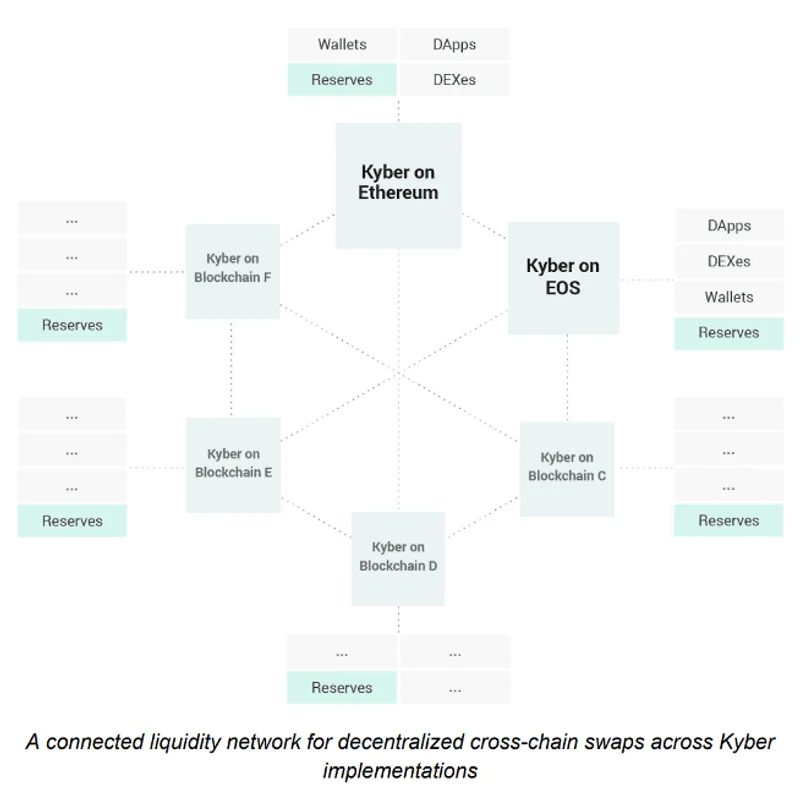
Users can receive the best return out of their transactions with Kyber, whether they are the ones initiating trades or providing liquidity.
- Quick Transaction Settlement: Through the help of smart contracts, traders can make orders and complete them with just a single transaction. Smart contracts are coded to complete a series of transactions without requiring the user to make multiple trading calls just to achieve their own objectives.
- Atomicity: Kyber does not allow transactions to be partially executed, differentiating them from centralized exchanges where users are exposed to the risk of their trading calls not being completely executed. With Kyber, it is either the trade is finalized wholly, or they do not get executed at all.
- Transparency: Anyone can launch a query from smart contracts to check the rates offered by liquidity providers. This gives the public the best transparency over their transactions.
- Interoperable: Since trades are trustless and atomic, they can be easily plugged into other smart contracts in the platform. This enables the network to simply execute trades through smart contract functions.
Network Actors
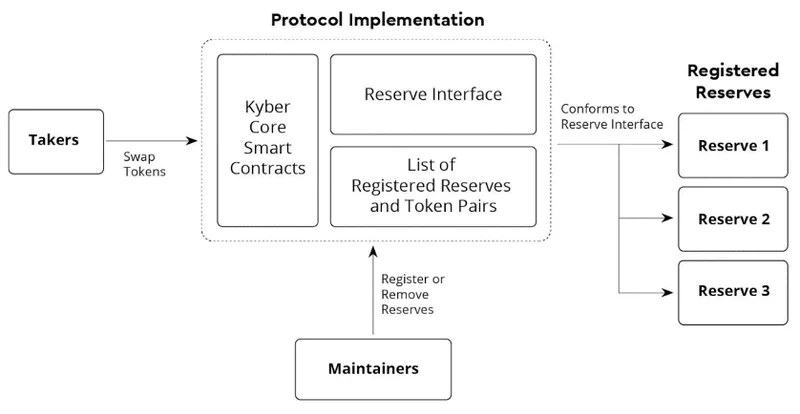
Kyber Smart Contracts: They are the backbone of the protocol, supporting functions such as listing and delisting of trading pairs, reserves, and queries, among others.
Takers: These can be any blockchain entity that gathers the liquidity coming from reserves listed within the network to facilitate trades from token-to-token.
Reserves: These are liquidity sources for the network that supply the token inventory and prices in Kyber’s smart contracts. Reserves determine the price for a particular asset as well as their supply.
Kyber Network Crystal Token ($KNC)
Kyber Network Crystal ($KNC) is Kyber’s economic, governance, and treasury token. KNC was launched in September 2017 with the aim to raise 200,000 ETH. The KNC token distribution is as follows: 61.06% to public; 19.47% to team; and 19.47% to founders, advisors and seed investors.
How KNC is used differs across chains. But mainly, here are the use cases for the KNC token:
- Economic Facilitation: KNC can be used to facilitate system operations, such as payments for every transaction made within the network, or to incorporate into the market spread. To get instant liquidity, users can also pay fees in KNC and get their transactions confirmed right away.
- Treasury Funds: The distribution of all KNC in total supply will include an allocation for the platform’s reserves. This reserve can be used by network maintainers and members of the DAO to fund network development. This is designed to support developers and network contributors by giving them an economic return for their work with KNC.
- Governance Token: Holding KNC gives users the chance to vote on important protocol decisions such as token parameters, network upgrades, and token listing, among others.
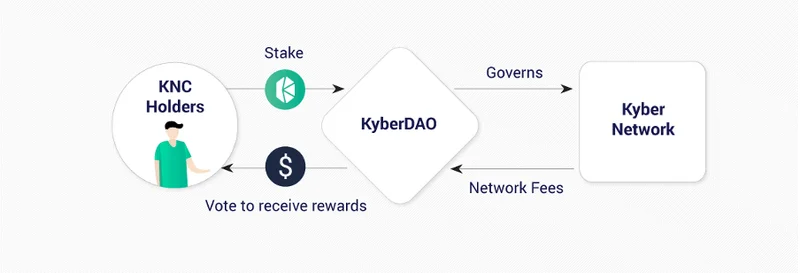
KyberDAO
KyberDAO, above all the things that have already been mentioned, incentivizes users to remain active in the network. But the following are key network parameters that KNC holders can vote upon:
- Voting Rewards: This is the allocated reward for stakers and governance participants.
- Burning: KNC holders can vote on whether to decrease the total supply of the KNC token.
- Reserve Incentives: This is the allocated reward for Kyber’s reserve managers.
As of now, Kyber is in charge of maintaining the DAO. They are facilitating community discussions, decision making, and execution of community decisions. This will remain so until more operational parameters in the network can be integrated with DAO votes.
Staking and Voting
There is a fixed period of time where users are allowed to stake and vote. These are called “epochs,” which is a denomination of Ethereum block times. Each epoch lasts for two weeks until the next cycle starts.
This allows Kyber to hasten the reward period for KNC holders and DAO participants, which also incentivizes them to vote within a fixed amount of time.
Delegating
If a KNC holder decides not to vote but keep a share in its rewards, they can delegate their voting power to another party who will do so on their behalf. They then retain their control of their KNC, which they can withdraw or use to transfer delegation to another party.
Conclusion
Many DeFi projects had their weaknesses exposed due to the volatility of crypto assets. However, Kyber Network is one of the few to have weathered the price instability of a lot of digital currencies in recent months.
So far, Kyber seems to be a very promising DeFi innovation that promotes a community-governed network. With the progress that it has made, Kyber is considered to be one of the toughest players in the DeFi space.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

