Ethereum has changed a lot since the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade began. Now fully running on Proof-of-Stake, the network is faster, cheaper, and uses way less energy. With sharding and other upgrades complete, Ethereum can handle over 100,000 transactions per second, making it a top choice for apps, games, and finance tools.
This article explains how Ethereum got here, what each upgrade did, and why it matters. Whether you’re new to crypto or already staking ETH, this guide will help you understand Ethereum’s journey and what’s next.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0—now simply called Ethereum—was a major upgrade that transformed the network from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake. This shift made Ethereum far more energy-efficient and scalable. The upgrade included several key milestones:
- The Merge (2022): Combined the original Ethereum mainnet with the Beacon Chain, switching the consensus mechanism to Proof-of-Stake.
- Sharding (Completed 2024): Split the network into multiple shards to boost speed and reduce costs. Ethereum now handles over 100,000 transactions per second.
- Staking: Users can earn passive income by staking ETH to help secure the network. As of mid-2025, staking yields average around 3.7% APR. Check out our staking guide HERE
These upgrades have made Ethereum faster, cheaper, and more accessible. Validators no longer need expensive hardware, and anyone can run a node—even from a laptop or phone. Ethereum now powers a massive ecosystem of DeFi apps, NFTs, and Web3 platforms, and continues to lead innovation in blockchain technology.
This guide will cover the timeline for the upgrade to ETH2.0 and the solutions proposed.
The 3 Phases of Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 2.0 will be launched in 3 phases:
- Phase 0- Beacon Chain – Completed in 2020
- Phase 1- The Merge – Completed September 2022
- Phase 2- Sharding
Ethereum 2.0—now simply Ethereum—was rolled out in three major phases, each transforming the network’s scalability, security, and sustainability:
Phase 0: Beacon Chain (Completed December 2020)
This phase introduced the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism via the Beacon Chain. It ran in parallel with the original Ethereum chain and laid the foundation for future upgrades by coordinating validators and generating randomness for staking.
Phase 1: The Merge (Completed September 2022)
The Merge combined the Beacon Chain with Ethereum’s mainnet, officially transitioning the network from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake. This reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by over 99.9% and eliminated the need for mining.
Phase 2: Sharding (Completed Q4 2024)
Sharding split Ethereum’s data processing across multiple chains (“shards”), dramatically increasing throughput and lowering costs. Combined with Layer 2 rollups, Ethereum now handles over 100,000 transactions per second. Validators can run nodes on lightweight devices, boosting decentralization and accessibility.
Main features of sharding:
Ethereum’s sharding implementation is now complete, delivering major improvements in scalability and decentralization:
- Lightweight Node Requirements: Validators no longer need to store the full blockchain. Thanks to data sampling and blob transactions, even mobile devices can run nodes.
- Greater Security via Decentralization: With over a million active validators, Ethereum is more resilient and censorship-resistant than ever.
- High Throughput: Combined with Layer 2 rollups, sharding enables over 100,000 transactions per second, significantly reducing gas fees.
- Efficient Data Distribution: Ethereum uses 64 shards to spread data across the network, minimizing congestion and improving performance.
- Optimized Rollup Integration: Rollups now directly access shard data, making them faster and cheaper, and enabling new use cases like real-time data feeds and decentralized AI.
What are layer 2 rollups?
Layer 2 rollups are scaling solutions that execute transactions off-chain and post compressed data back to Ethereum, reducing congestion and lowering fees. As of 2025, rollups have matured into the backbone of Ethereum’s scalability strategy.
- Optimistic and ZK Rollups: Both types are widely adopted. ZK rollups, in particular, have gained traction for their speed and security, powering applications in DeFi, gaming, and identity verification.
- Blob Transactions and Proto-Danksharding: Introduced in the Cancun-Deneb upgrade, blob-carrying transactions allow rollups to post large data payloads efficiently. This has drastically reduced costs and improved throughput.
- Rollup-Centric Ethereum: Ethereum now functions as a data availability and settlement layer, while most user activity occurs on rollups. This architecture supports over 100,000 transactions per second.
- Interoperability and Composability: Rollups are increasingly interoperable, allowing seamless asset transfers and smart contract interactions across different Layer 2s.
- Decentralized Applications at Scale: From social media platforms to real-time multiplayer games, rollups have enabled dApps that were previously impossible on Layer 1 due to cost and latency.
Learn more: Understanding layer 2 & scaling solutions: Arbitrum, Boba, Optimism, Polygon, Ethereum 2.0
What is the current state of Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0—now simply referred to as Ethereum—has completed its major transition phases and entered a new era of scalability and decentralization. Here’s a snapshot of its current state:
- Proof-of-Stake Fully Operational: Since the Merge in September 2022, Ethereum has run entirely on Proof-of-Stake. Validator participation remains high, with over 1 million active validators and a network participation rate consistently above 99%.
- Sharding Completed: As of late 2024, Ethereum successfully launched 64 shards, dramatically improving data throughput and enabling lightweight node operation. This has made it possible to run validator nodes on consumer-grade devices.
- Rollup-Centric Architecture: Most user activity now occurs on Layer 2 rollups, which post data back to Ethereum using blob transactions introduced in the Cancun-Deneb upgrade. This architecture supports over 100,000 transactions per second.
- Post-Merge Upgrades: Ethereum has progressed through the “Surge” (scaling via sharding), and is actively implementing the “Scourge,” “Verge,” “Purge,” and “Splurge”—a series of upgrades focused on censorship resistance, stateless clients, historical data cleanup, and protocol refinement.
- Staking and Withdrawals: Withdrawals have been enabled since the Shanghai (Shapella) upgrade in April 2023. Staking remains popular, with yields averaging 3.5–5% annually depending on network conditions.
- EVM Improvements: The Ethereum Virtual Machine has seen multiple enhancements, including support for Verkle trees and EOF (EVM Object Format), improving efficiency and developer experience.
How to set up an Ethereum Validator Node
Check out our LIVE demonstration on how to set up an Ethereum 2.0 Node
I’ve also set up something called an Ethereum validator node for Ethereum 2.0. These nodes will be how Ethereum would run and how transactions are going to be validated in the future. So we’re going to explore all of these concepts as well in this guide.
Currently you can test out Ethereum staking on the ETH 2.0 Testnet set up by Prysmatic labs (aka Topaz). Since it’s a test, Ethereum will not be used, instead, it will use Göerli ETH, a free testnet version of ETH.
Time needed: 2 days
How to set up an Ethereum (ETH) Validator Node
This guide has been adapted from the Prysm ‘Topaz’ Testnet Guide
Göerli ETH is free to obtain and will be used to stake the 32 ETH required for the node. The easiest way to obtain the Göerli ETH is to use the social faucet.
You’ll need to be familiar with running a VPS server (you can use AWS, Hetzner or Linode). Recommended specs include an Intel Core i7 processor with 100 GB of SSD storage
Easiest way we found to do this is via Docker
docker run -it -v $HOME/prysm/beacon:/data -p 4000:4000 -p 13000:13000 \ gcr.io/prysmaticlabs/prysm/beacon-chain:latest \ –datadir=/data
docker run -it -v $HOME/prysm/validator:/data \ gcr.io/prysmaticlabs/prysm/validator:latest \ accounts create –keystore-path=/data
Complete the steps here to stake the ETH
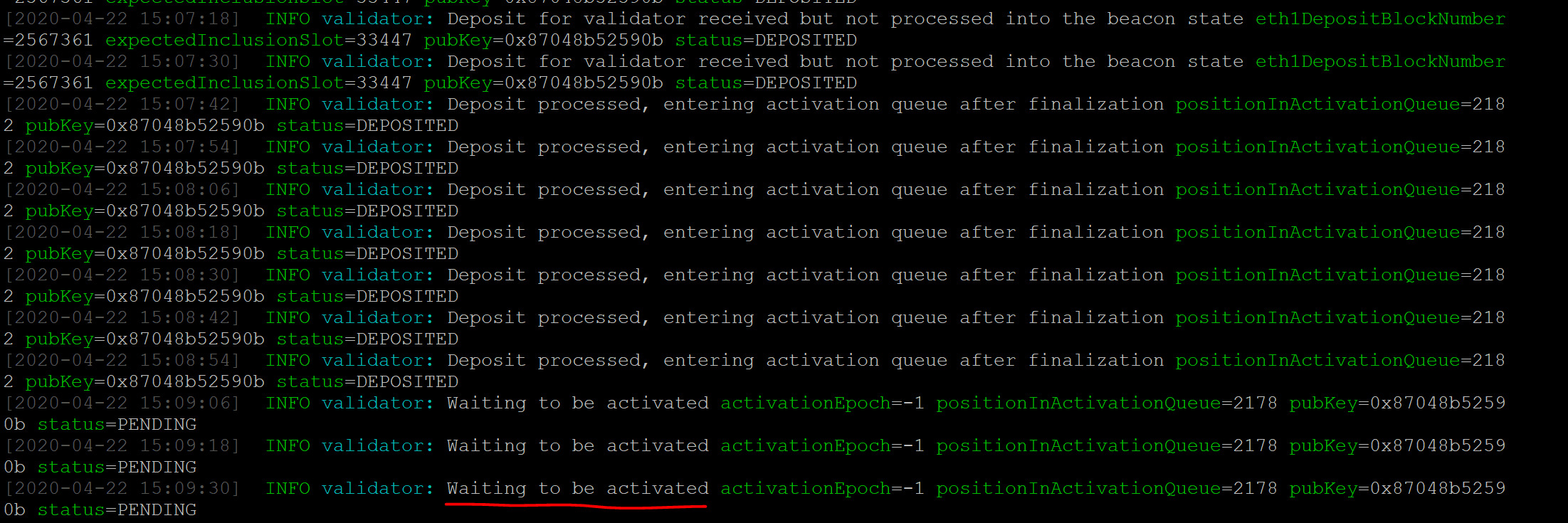 Finish the activation
Wait (roughly 2 days) to get activated, and then you’re good to go!
Finish the activation
Wait (roughly 2 days) to get activated, and then you’re good to go!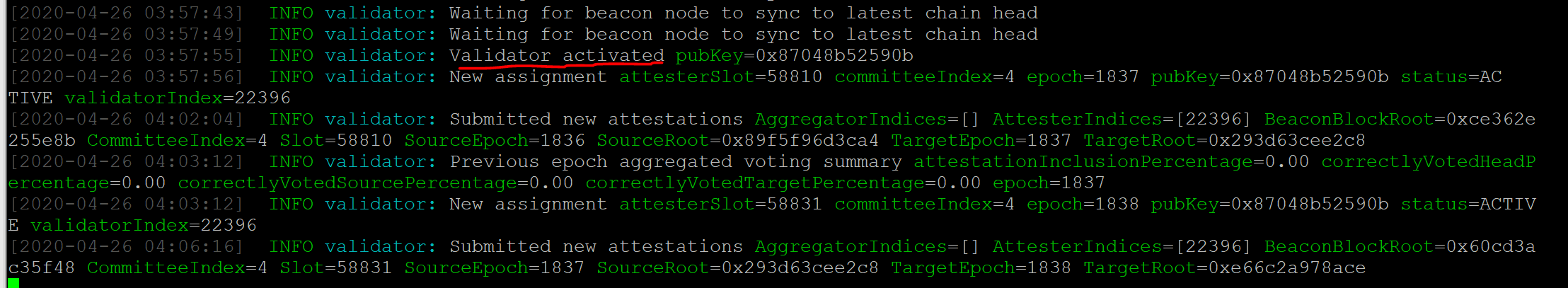
Staking Ethereum on a validator node
Ethereum now operates fully under Proof-of-Stake, and staking remains a core mechanism for securing the network and earning passive income.
- Stake Requirement: 32 ETH is required to activate a validator. This stake acts as collateral to ensure honest behavior and network uptime.
- Rewards: Annual staking yields range from 3.5% to 5%, depending on network conditions and validator performance. Rewards are paid in ETH and accumulate over time.
- Withdrawals: Since the Shanghai (Shapella) upgrade in April 2023, stakers can withdraw both principal and rewards. Withdrawals are processed in queue and typically take hours to days.
- Risks: Validators face penalties for downtime or incorrect attestations. Slashing is rare but possible in cases of malicious behavior or prolonged inactivity.
- Network Health: As of August 2025, over 1 million validators are active, and more than 30 million ETH is staked. Participation rates consistently exceed 99%, ensuring robust security.
- Liquid Staking Options: For users with less than 32 ETH or those seeking flexibility, platforms like Lido, Rocket Pool, and Coinbase offer tokenized staking (e.g. stETH, rETH) with instant liquidity and pooled validation.
Ethereum Staking: Deposit contract address release
The Ethereum staking deposit contract was officially released on November 4, 2020, marking the beginning of Phase 0 and enabling users to stake ETH and become validators. While the original launch required careful navigation through the Ethereum Launchpad, staking has since become more streamlined and widely accessible.
As of 2025:
- Deposit Contract Still Active: The original deposit contract remains the gateway for validator activation. Users must still follow the Launchpad process to generate keys and deposit 32 ETH securely.
- Withdrawals Enabled: Since the Shanghai (Shapella) upgrade in April 2023, stakers can withdraw both rewards and principal. This has made staking more flexible and liquid.
- Validator Growth: Over 1 million validators are now active, with more than 30 million ETH staked. Participation rates consistently exceed 99%, ensuring strong network security.
- Liquid Staking Alternatives: Platforms like Lido, Rocket Pool, and Coinbase offer pooled staking and tokenized derivatives (e.g., stETH, rETH), allowing users to stake without the full 32 ETH requirement.
- Security Reminder: Sending ETH directly to the deposit contract without using the Launchpad will still result in a failed transaction. Proper setup remains essential to avoid loss of funds or penalties.
Ethereum Staking Update: Yields?
Ethereum staking yields have stabilized following the full rollout of Proof-of-Stake and the Shanghai upgrade, which enabled withdrawals in April 2023.
Risk Factors: While slashing remains rare, validators must maintain uptime and correct behavior to avoid penalties. Liquid staking platforms typically abstract these risks for users.
Current APR: As of August 2025, the average annual percentage return (APR) for staking ETH ranges between 3.5% and 4.2%, depending on validator performance and network activity.
Yield Trends: Early stakers enjoyed higher returns (up to 16% pre-Merge), but yields have normalized as validator participation increased. Over 30 million ETH is currently staked, with more than 1 million active validators.
Liquid Staking: Tokenized staking options like stETH (Lido), rETH (Rocket Pool), and cbETH (Coinbase) offer competitive yields and instant liquidity, making them popular among users with less than 32 ETH.
Rewards Distribution: Staking rewards are paid in ETH and accumulate continuously. Validators earn from proposing blocks, attesting to others, and participating in sync committees.
You can check the current APR, total ETH staked, and number of validators here.
Progress of Ethereum 2.0 so far
Ethereum 2.0—now simply Ethereum—has completed its major upgrade phases and transitioned into a scalable, energy-efficient, and decentralized network. Here’s a summary of its progress:
- Beacon Chain (Phase 0): Launched in December 2020, introducing Proof-of-Stake and laying the foundation for future upgrades.
- The Merge (Phase 1): Completed in September 2022, merging the Beacon Chain with Ethereum’s mainnet and eliminating Proof-of-Work. This reduced energy consumption by over 99.9%.
- Sharding (Phase 2): Rolled out in late 2024, Ethereum now operates with 64 shards, enabling lightweight node operation and dramatically increasing data throughput.
- Post-Merge Upgrades: Ethereum has entered the “Surge,” “Scourge,” “Verge,” “Purge,” and “Splurge” phases—targeting scalability, censorship resistance, stateless clients, historical data cleanup, and protocol refinement.
- Network Metrics: As of August 2025, over 30 million ETH is staked across more than 1 million validators. Participation rates remain above 99%, ensuring strong consensus and security.
- Rollup-Centric Architecture: Most user activity now occurs on Layer 2 rollups, which leverage blob transactions for efficient data posting. Ethereum supports over 100,000 transactions per second.
What’s next in the development of Ethereum 2.0?
With the Merge and Sharding now complete, Ethereum has entered the post-2.0 era, focusing on refinement, decentralization, and long-term sustainability.
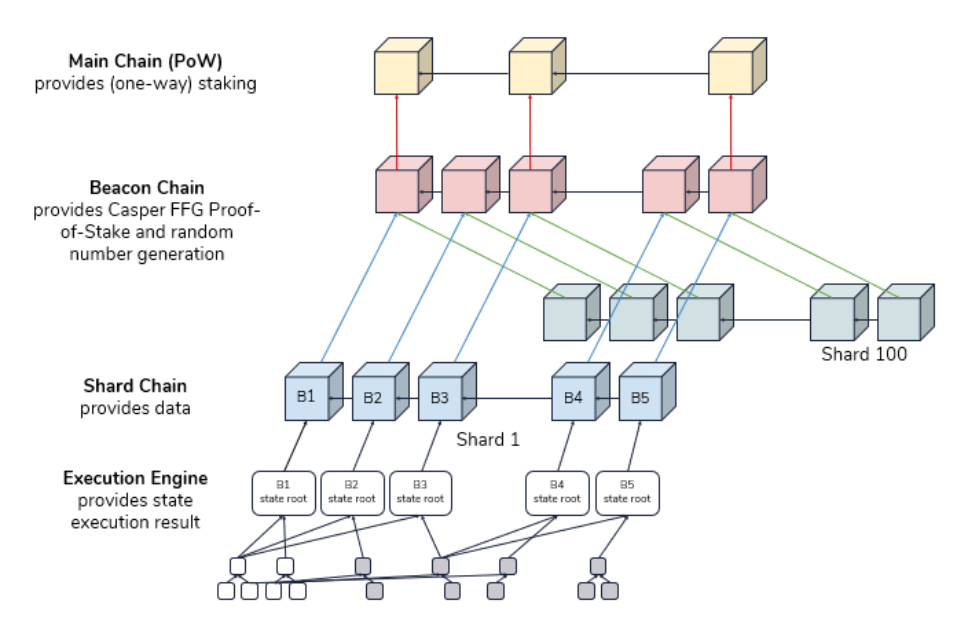
The roadmap outlined by Vitalik Buterin continues through five major upgrade phases:
- The Surge: Completed in late 2024, this phase introduced sharding and significantly boosted scalability. Ethereum now supports over 100,000 transactions per second, primarily through rollups.
- The Scourge: Currently underway, this phase addresses MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) risks and aims to ensure fair, neutral transaction inclusion. Protocol-level changes are being tested to reduce centralization in block production.
- The Verge: Focused on stateless clients and Verkle trees, this phase will allow validators to operate without storing full blockchain data. It’s expected to launch in stages through 2026, improving decentralization and node efficiency.
- The Purge: Aimed at reducing historical data bloat, this phase will simplify node operation by removing unnecessary legacy data. It will also streamline the Ethereum protocol for developers.
- The Splurge: A collection of smaller upgrades and optimizations, including EVM improvements, fee market refinements, and UX enhancements. These updates are ongoing and released incrementally.
What will happen after ETH 2.0 is launched?
Ethereum 2.0 is no longer a future milestone—it’s now fully integrated into the Ethereum protocol. The network has transitioned from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake, implemented sharding, and embraced a rollup-centric architecture. Here’s what has unfolded since the launch:
- Scalability Achieved: Ethereum now supports over 100,000 transactions per second through a combination of sharding and Layer 2 rollups. This has eliminated congestion and dramatically reduced gas fees.
- Energy Efficiency: The network consumes over 99.9% less energy than it did under Proof-of-Work, making Ethereum one of the most sustainable major blockchains.
- Validator Participation: Over 1 million validators are active, securing the network with more than 30 million ETH staked. Lightweight node requirements have enabled broader participation.
- Rollup Dominance: Most user activity now occurs on Layer 2 platforms like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync. Ethereum Layer 1 serves primarily as a settlement and data availability layer.
- Reduced Competition from “Ethereum Killers”: With its scalability and efficiency challenges resolved, Ethereum has maintained its dominance in DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 infrastructure. Competing chains have shifted focus to niche use cases or interoperability.
- Ongoing Upgrades: Ethereum is now progressing through the “Scourge,” “Verge,” “Purge,” and “Splurge” phases, which aim to improve censorship resistance, decentralization, protocol simplicity, and developer experience.
Eventually, the number of transactions per second will drastically increase to over 100,000 tps. So, the question would be, what would happen to the competition i.e. the “Ethereum killers”? Find out more in our article: Ethereum Merge is coming, is this the end of Ethereum killers?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
No. Ethereum 2.0 was a series of upgrades that merged into the existing Ethereum network. The term is now outdated—Ethereum runs on Proof-of-Stake and sharding, but it’s still the same ETH.
No new coin was created. ETH remains the native currency. Beware of scams offering “ETH2” tokens—they don’t exist.
Yes. Since the Shanghai (Shapella) upgrade in April 2023, both staking rewards and principal can be withdrawn.
As of August 2025, staking yields range from 3.5% to 4.2% annually, depending on network activity and validator performance.
Not necessarily. While 32 ETH is required to run a validator node, liquid staking platforms like Lido, Rocket Pool, and Coinbase allow staking with smaller amounts.
Staking is generally safe, but validators can be penalized for downtime or malicious behavior. Liquid staking abstracts most of these risks for casual users.
Yes. With sharding and rollups fully deployed, Ethereum can process over 100,000 transactions per second, significantly reducing gas fees.
Yes. Thanks to sharding and protocol optimizations, validators can now run on laptops or even mobile devices.
Mining ended with the Merge in September 2022. Ethereum now uses Proof-of-Stake, and mining is no longer part of the protocol.
No major disruptions occurred. Most exchanges and dApps transitioned smoothly during the upgrades.
Tax implications vary by country. In general, staking rewards are considered income and may be taxable when received.
Ethereum is progressing through the Verge, Purge, Scourge, and Splurge phases—focused on decentralization, data cleanup, MEV mitigation, and protocol refinement.
Further reading
Ethereum Foundation: https://ethereum.org/en/upgrades
Pyrsmatic Labs: https://medium.com/prysmatic-labs/how-to-scale-ethereum-sharding-explained-ba2e283b7fce
Ethereum Wallet holders: https://bitinfocharts.com/comparison/activeaddresses-eth.html
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

Michael Gu
Michael Gu, Creator of Boxmining, stared in the Blockchain space as a Bitcoin miner in 2012. Something he immediately noticed was that accurate information is hard to come by in this space. He started Boxmining in 2017 mainly as a passion project, to educate people on digital assets and share his experiences. Being based in Asia, Michael also found a huge discrepancy between digital asset trends and knowledge gap in the West and China.
