CertiK aims to provide a secure platform where blockchain infrastructure and decentralized applications can be developed. Its ecosystem consists of security layers that exist below the blockchain level, including the DeepSEA compiler, the CertiK Virtual Machine (CVM), and CertiKOS. Its native token, $CTK, has launched in Binance Launchpool on 27 October 2020. Below is a detailed overview of the CertiK ecosystem, including the CertiK chain.
Background
The CertiK Foundation supports the CertiK platform. The organization champions trust in blockchain systems. Its efforts are displayed through the development of a secure network that can boost confidence in decentralized systems. Furthermore, the CertiK Foundation is lead by renowned computer professors.
What is CertiK?
CertiK is a decentralized smart contract platform powering Dapps. Additionally, it supports inter-chain communication and runs on the Certik Chain.
The system is primed for highly-specialized use cases. The protocol employs a PoS variation called delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) and uses the Cosmos software development kit (SDK).
The CertiK Foundation has taken upon itself to restore the trust in distributed platforms by employing cutting-edge security technologies and techniques. A key milestone achieved by CertiK is the provision of provable trust in a decentralized platform. Apart from focusing on security, the network also addresses performance and token economics.
CertiK Token ($CTK)
The economic aspect of the platform relies on the platform’s native currency, CTK. CTK’s major offering is being a utility token. (Provigil) Therefore, it helps power the crucial aspects of the CertiK ecosystem.
For example, the token provides a mode of payment and settlement among the platform’s users.
However, the token does not give its holders the right to interact and does not act as an investment into CertiK Foundation. Being issued inside a PoS-powered system, the token carries various benefits to incentivize holders to participate in staking and securing the network.
Apart from being used on the CertiK protocol, CTK is a significant ingredient in the CertiK Chain. Here, the token is used to pay for transaction fees.
In return, the fees reward staking nodes on the chain. Also, the token is used to reward those who delegate their CTK holding to validator nodes.
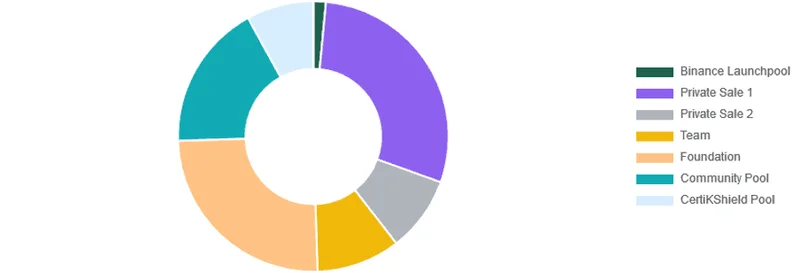
The token’s first issuance was achieved through two private sales that sold a total of 38 million CTK tokens worth a cumulative $39,430,000. Apart from the private sale 1 & 2 (29.0% & 9.0% respectively), the token distribution allocated 1.5% of its total supply to Binance Launchpool, 10.0% to the CertiK team, 25% to the CertiK Foundation, 17.5% to the community pool, and 8.0% to the CertiKShield pool.
What is CertiK Chain?
CertiK Chain is a blockchain protocol powering the CertiK ecosystem. It is highly secure and has cross-chain interoperability. To effectively achieve its mission, the platform incorporates key components such as a security oracle and a CertiKShield pool.
Let’s dig into each of these components.
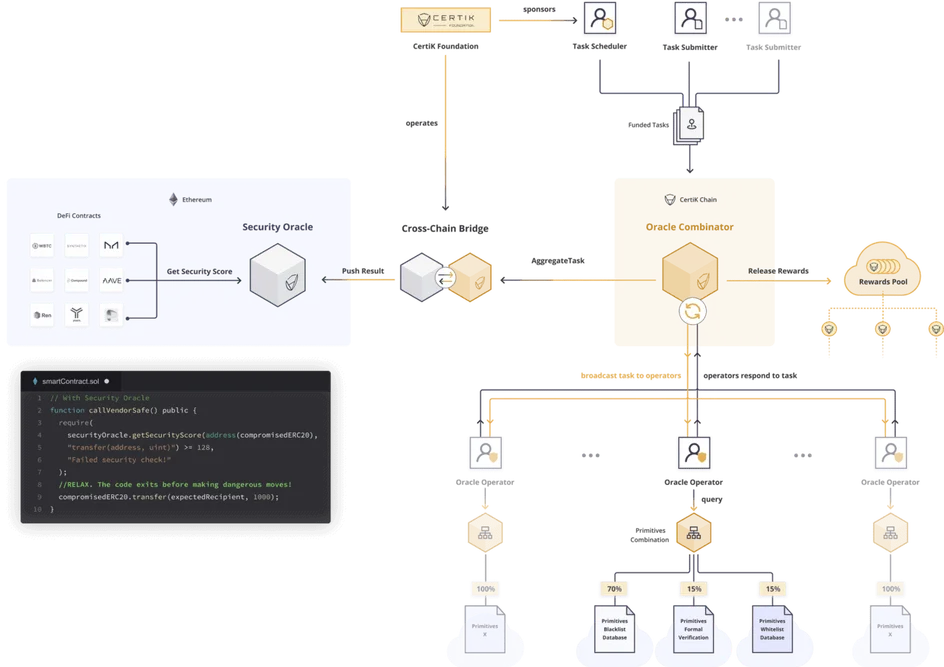
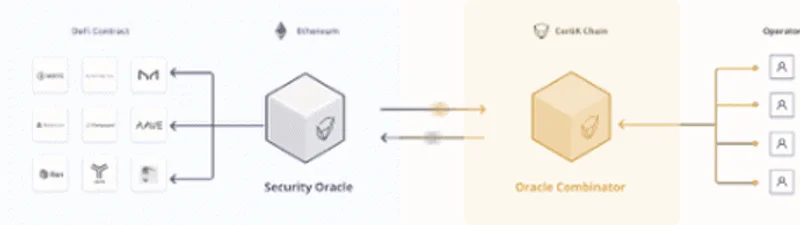
CertiK’s Security Oracle
The platform’s security oracle compresses audit reports to make them available on-chain. Basically, audit reports hold information as to the reliability of smart contracts. But, the reliability of smart contracts can be sabotaged by the data it uses to make decisions.
With these reports living outside blockchain platforms, it poses a security threat prompting CertiK to bring them on-chain through its security oracle. Consequently, the network can effectively verify the security of a smart contract.
Note that this component allocates scores depending on a smart contract’s latest audit report. The scores give an overview of a contract’s code reliability.
More than just scoring contracts, the security oracle can track and report unaudited smart contracts. A distributed security team handles such reports. Using the CertiK Oracle Combinator, results from the security team are aggregated into a single score that can be accessed online. And, of course, the security team is rewarded.
Luckily, this functionality is crucial in a decentralized finance (DeFi) setting where unaudited smart contracts are wreaking havoc. For example, by incorporating the CertiK’s security oracle, the responsibility of an audit is shifted from the contract creator to the contract users.
CertiKShield Pool
The CertiKShield pool is a unique component meant to minimize the risks emanating from the private nature of (most) cryptocurrencies. This may include losses from both avoidable and unavoidable circumstances such as house fires.
The shield works by providing a flexible pool of CTK tokens. Since the token uses on-chain governance mechanisms, it can be used to compensate losses sprouting from inaccessibility and/or theft.
In other words, this operates as an insurance platform. But, its decentralized nature allows it to receive inputs from all involved individuals before settling a claim.
The CertiKShield Pool is made up of collateral providers and shied purchasers. Collateral providers earn staking rewards while shield purchasers pay for requested protection.
CertiK Chain Architecture
The main components of the CertiK Chain are baked together in an architecture that can achieve provable trust. Apart from the security oracle and the shield pool, the network’s backbone comprises a virtual machine and the DeepSEA toolchain.
CertiK Virtual Machine (CVM)
The CVM effectively eliminates the errors that may be introduced when converting smart contract code from human-based language to machine language. Although these errors may be unknown to contract developers, they pose a severe security risk.
Being a security-first decentralized platform, the CVM relies on the output of DeepSEA, a certified compiler. The compiler’s output includes bytecode and mathematical proofs. The proofs can be used to isolate smart contracts’ code that doesn’t meet the security standards.
DeepSEA Toolchain
DeepSEA is a compiler and a programming language that’s hailed for its security. Notably, the CertiK-native tool is developed in conjunction with researchers from leading learning institutions such as Columbia and Yale University.
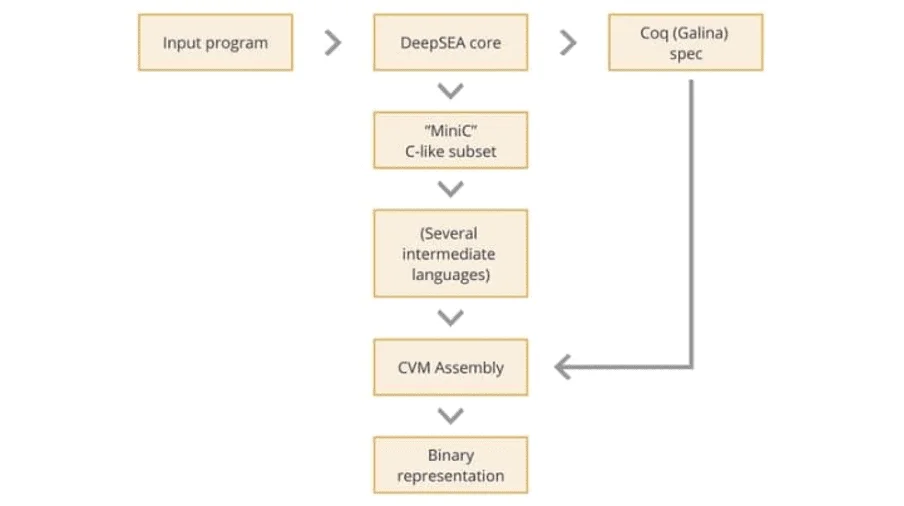
The toolchain can determine the complex correctness properties of smart contracts. As such, it enhances the security of the network and products built on top of it.
CertiK Governance
The CertiK protocol uses on-chain governance methods to enable community involvement in decision-making. However, to vote for proposals, CTK holders can either delegate their voting powers to validators or vote directly. Validator nodes ensure the smooth running of the platform through powering activities such as block production.
CertiK accommodates five types of proposals from its community:
- Plain text: These are proposals that request modification of things like altering the number of incentives paid to validators.
- Software upgrade: They lead to code modifications. They may include proposals to add new features.
- Bounty: Examples of proposals in this category include those touching on creating chain artifacts and conducting security audits.
- Community pool spend – They cater for the transfer of funds from a pool to an individual address, for instance, an individual developing a CertiK-specific product or upgrade.
- Certifier: They are submitted by a certifier with a request to add or remove a certifier. Note that certifiers and validators vote on proposals.
Conclusion
In a space where malicious actors are always on the prowl for weaknesses in DeFi-focused smart contracts, CertiK provides the much-needed peace of mind. In addition, enabling a decentralized contract audit removes the need for DeFi users to solely rely on reports provided by the team, which, in some cases, are anonymous.
From the security oracle to the reimbursement pools, to DeepSEA, the network structurally achieves a security-first approach with provable trust.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

