Ethereum remains the backbone of decentralized finance, but even after its shift to proof-of-stake, scalability issues persist. Polygon has emerged as a leading layer-2 solution, offering faster, cheaper transactions through a growing suite of tools like zkEVMs, Optimistic rollups, and modular sidechains.
Originally launched as Matic Network, Polygon now powers a vast ecosystem of DeFi apps, games, and enterprise platforms. Its SDK enables developers to build scalable, secure chains with minimal friction, while the MATIC token supports staking and transaction fees. In 2025, Polygon is not just supporting Ethereum—it’s helping redefine its future.
Background
Polygon began its journey as Matic Network, a solution aimed at accelerating blockchain transactions and making them more accessible. Initially focused on general scalability, the project pivoted toward Ethereum, evolving into a layer-2 scaling solution provider. With this shift came a rebrand to Polygon.
Founded by Jaynti Kanani, Anurag Arjun, and Sandeep Nailwal—later joined by Mihailo Bjelic—the team envisioned a future where blockchain technology would seamlessly connect humans and machines. Their early efforts culminated in a seed round in August 2019, backed by MiH Ventures.
Since the release of Polygon SDK v1 in March 2021, the platform has undergone significant evolution. By 2025, Polygon has become a cornerstone of Ethereum’s scaling strategy, especially as Ethereum 2.0 continues its phased rollout. Polygon’s suite now includes zkEVM (zero-knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine), which launched in 2023 and has gained traction for its ability to offer Ethereum-compatible smart contracts with enhanced scalability and privacy.
Polygon Labs, the development arm, has also expanded its ecosystem through strategic acquisitions and partnerships, including integrations with major Web3 platforms and enterprise blockchains. The team has focused heavily on modularity, enabling developers to choose between various scaling architectures—Optimistic rollups, zk-rollups, and validium chains—depending on their needs.
In 2025, Polygon is not just a scaling solution but a multi-chain ecosystem builder, with its technology underpinning thousands of decentralized applications (dApps) across DeFi, gaming, and enterprise sectors. Its commitment to Ethereum compatibility, developer accessibility, and security modularity continues to position it as a leader in blockchain infrastructure.
What is Polygon ($MATIC)?
Polygon is a modular framework designed to scale Ethereum by enabling faster, cheaper, and more flexible blockchain development. Originally launched as Matic Network, it has evolved into a full-fledged layer-2 ecosystem supporting a wide range of scaling solutions—including zkEVM chains, Optimistic rollups, and app-specific sidechains.
At its core is the Polygon SDK, which allows developers to build custom chains that are interoperable with Ethereum. These chains can be secured independently or leverage shared security from Ethereum or third-party validator networks. Polygon’s infrastructure now supports thousands of decentralized applications across DeFi, gaming, and enterprise use cases.
In 2025, Polygon is more than just a scaling tool—it’s a key pillar in Ethereum’s multi-chain future. Its native token, MATIC, continues to power transactions and staking across the network, while Polygon’s developer tools have become essential for building scalable, user-friendly Web3 applications.
Advantages of Polygon
Here are some of the major advantages of Polygon.
Scalability and Speed
Polygon continues to deliver on its promise of scaling Ethereum. With production-grade zkEVM chains and Optimistic rollups now widely adopted, transaction speeds have reached near-instant levels, and gas fees remain consistently low. This has enabled developers to build high-performance dApps without compromising on user experience or cost efficiency.
Developer-Friendly Infrastructure
Polygon’s SDK has matured into a modular toolkit that supports rapid deployment of custom chains. Developers can now choose between stand-alone chains with independent security or secured chains leveraging Ethereum or third-party validator networks. The WebAssembly (WASM) environment and plug-and-play architecture make it easy for teams—even those without deep blockchain expertise—to launch scalable applications.
Security and Flexibility
Polygon’s “security as a service” model allows developers to select their preferred security layer, whether it’s Ethereum’s native validators or external professional pools. This flexibility ensures that chains can be tailored to specific use cases without sacrificing safety. All Polygon-based products remain fully compatible with Ethereum, preserving interoperability across the ecosystem.
User Experience
For end users, Polygon offers fast, low-cost transactions and intuitive interfaces. The network now supports seamless token swaps, smart contract interactions, and oracle integrations, making it a go-to platform for DeFi, gaming, and enterprise applications. These improvements have helped onboard millions of new users to Web3.
Ecosystem Growth
By 2025, Polygon has become a foundational layer for Ethereum’s multi-chain future. Its infrastructure supports thousands of active dApps, and its developer community continues to expand. Major brands, financial institutions, and governments are now exploring Polygon for scalable blockchain deployments.
Polygon Chains
Polygon’s architecture has evolved significantly since its early days as Matic Network. Initially built on the Plasma framework, which allowed sidechains to operate semi-independently from Ethereum, Polygon has grown into a modular, multi-chain ecosystem tailored to diverse blockchain use cases.
As of 2025, Polygon supports three primary chain types:
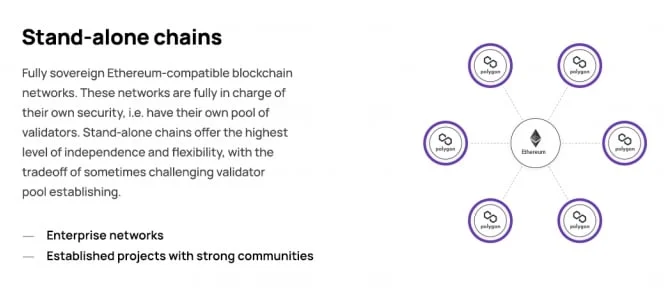
Stand-alone Chains
These chains operate independently and manage their own security. They are ideal for projects that require full control over their validator set and consensus mechanisms. Common use cases include gaming platforms and enterprise blockchains that prioritize performance and customization over shared security.
- Security: Self-managed validator pools
- Use Cases: High-performance decentralized applications (dApps), private enterprise solutions
- Examples: Polygon PoS (still active but gradually being phased out in favor of zk-based chains)
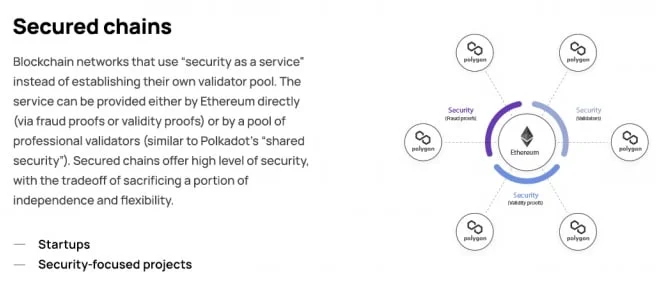
Secured Chains
Secured chains outsource their security to Ethereum or other trusted validator networks. This model has gained popularity due to its simplicity and strong trust assumptions.
- Security: Ethereum-based fraud proofs, validity proofs, or third-party validator services
- Use Cases: DeFi protocols, public infrastructure dApps
- Examples: Polygon zkEVM, chains built using the Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK)
zk-Rollup Chains
Polygon’s most transformative innovation has been its zero-knowledge (zk) rollup technology. With the launch of Polygon zkEVM in 2023 and the release of the CDK in 2024, developers can now deploy custom zk-powered chains that are Ethereum-compatible, scalable, and privacy-preserving.
- Security: Inherited from Ethereum via zk proofs
- Use Cases: Scalable DeFi, identity solutions, cross-chain bridges
- Features: Native EVM compatibility, low latency, high throughput
MATIC token
MATIC remains the native utility and governance token of the Polygon ecosystem, but its role has expanded significantly since its early use for transaction fees and staking.
Core Functions
- Transaction Fees: MATIC continues to be used for paying gas fees across Polygon chains, including zkEVM and CDK-based rollups.
- Staking & Validation: Validators stake MATIC to secure Polygon’s proof-of-stake chains, although many newer chains now rely on Ethereum-based security via zk proofs.
- Governance: MATIC holders participate in on-chain governance, influencing protocol upgrades, treasury allocations, and ecosystem grants.
Evolution Since 2023
- zkEVM Integration: With the rise of zkEVM and modular chain deployments, MATIC has been integrated into fee markets and bridge mechanisms, allowing seamless movement between Ethereum and Polygon-based chains.
- Deflationary Pressure: A portion of transaction fees on certain chains is now burned, introducing deflationary dynamics similar to Ethereum’s EIP-1559 model.
- Cross-Chain Utility: MATIC is increasingly used as collateral and liquidity across DeFi protocols on other chains, including Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base, thanks to improved interoperability.
Market Position in 2025
Institutional Interest: Polygon Labs has secured partnerships with enterprise clients in gaming, supply chain, and identity sectors, boosting MATIC’s utility beyond retail DeFi.
Price Volatility: MATIC has experienced fluctuations due to broader market cycles and competition from other layer-2 tokens, but remains a top-30 crypto asset by market cap.
Conclusion
Polygon has evolved from a promising Ethereum sidechain into a foundational layer of the Ethereum scaling ecosystem. Its modular architecture, developer-friendly tools, and pioneering work in zero-knowledge technology have positioned it as a leader in the multi-chain future of Web3.
In 2025, Polygon is no longer just a workaround for Ethereum’s limitations—it’s a robust platform enabling scalable, secure, and interoperable blockchain networks. The launch of Polygon zkEVM and the Chain Development Kit (CDK) has empowered developers to build custom rollups with native Ethereum compatibility, while maintaining high throughput and low costs.
Polygon’s vision of a seamlessly connected blockchain world is materializing through its growing network of zk-powered chains, enterprise integrations, and developer adoption. As Ethereum 2.0 continues its rollout, Polygon complements it by offering flexible scaling solutions that serve both public dApps and private infrastructure.
In a rapidly evolving crypto landscape, Polygon remains a critical pillar for Ethereum’s long-term scalability, usability, and mass adoption.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

