CUDOS aims to let users sell their excess computing resources through a collaborative consumption network platform.
In the over 11 years since the launch of the first blockchain, Bitcoin, we have seen a need to connect decentralized networks with real-world data to spur the networks’ usage. The first solution is to introduce layer 2 chains to process transactions before committing them on the underlying immutable protocols.
However, in the rapidly changing blockchain and physical world, we need a platform that is Turing complete, unlike Bitcoin. One that can handle virtually anything we throw at it without hitting a memory or processing power bottleneck. This is what CUDOS aims to do.
Background
In 2017 Matt Hawkings founded the CUDOS protocol. In the past, Hawkings worked in different technology companies in various capacities, such as being the chief technical officer of CORETX and the managing director of C4L.
Other team members include Andrew Sturmey (CTO), Pete Willis (Development Manager), Joan Garcia I Tormo (Data Scientist), and Richard Poole (Lead Developer/ Architect). The development team works under Cudo Ventures.
Notably, the project’s advisors come from reputable firms such as AMD, Sony Entertainment, and ESET UK.
What is CUDOS?
The CUDOS network is a decentralized layer two chain bringing cloud computing functionalities to decentralized platforms.
CUDOS uses a group of smart contracts that sit at the center of the computing functionalities. Also, the smart contract acts as oracles to interface off-chain data with blockchains and vice versa.
Since blockchains use different programming languages, CUDOS’ Turing completeness enables data processing for a wide range of distributed protocols regardless of their underlying programming language. This means that you can process data for Python and Go-programmed networks with ease.
How CUDOS Works
To incorporate Turing-completeness and merge blockchain and cloud computing, CUDOS uses validator nodes known as CVNs (CUDOS Validator Nodes).
Smart contracts allow blockchain developers to interact with CVNs by specifying the number of validator nodes to process their desired data.
The benefit of this approach is that it enables developers to choose the ideal configuration depending on the task at hand.
Where a task spreads across multiple nodes, the nodes share individual results with each other for consensus. Note that agreement can either be conducted outside or inside the blockchain. Off-chain consensus minimizes the transaction costs.
Notably, to be eco-friendly, the project taps into the idle computing power of data centers and other computing devices that would wish to contribute their power to earn incentives.
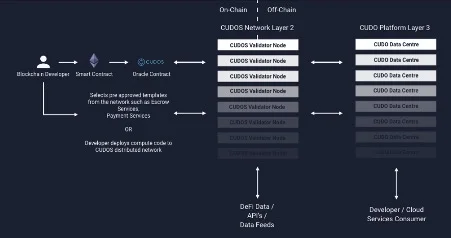
On the surface, a developer interacts with Ethereum smart contracts, which in turn pings to the CUDOS oracle contract. From here, it connects to validator nodes, either on-chain or off-chain. Validator nodes then interface with CUDO data centers that operate on top of the CUDOS platform.
CUDOS Use Cases
Being Turing complete means the platform can process almost anything. Consequently, this expands CUDOS’ use cases. At its basic structure, the network can be used as a layer two oracle to deliver data to and from smart contracts.
Furthermore, its computing capabilities make it a perfect fit for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, scientific research, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and video rendering.
Advantages of Using CUDOS
CUDOS has numerous benefits due to its unique approach of connecting off-chain and on-chain systems. Key among them include;
- Efficiency enhancement – The protocol improves efficiency for developers to optimize workflows and improve the accuracy of results.
- Cost Reduction – It is estimated that CUDOS’ users save more than 75% compared to when using traditional cloud computing services.
- Flexible management – With CUDOS, you decide how much computing power you need; there are no limits. In addition, it allows users to compute how much processing power they need before running a task.
CUDOS’ Token (CUDOS) and Governance
Interestingly, the network and its native token share the same name, CUDOS.
CUDOS token use cases
The CUDOS token has 3 main use cases.
- Gaming: The Cudo platform allows gamers to rent out their spare computational capacity for tasks such as video rendering, AI computing and scientific research. CUDOS tokens are given as a reward for their efforts. These can then be used to access others’ excess computing resources so they can play games that push their hardware past its limits.
- Charity: Users can donate their computer’s idle resources to charity. Currently, cryptocurrency miners can use Cudo to contribute the tokens they have mined into their selected charity’s preferred payout currency and deliver this to the charity.
- Staking: The CUDOS token can be staked to participate in securing the network.
Note that stakers’ rewards emanate from revenues generated on the protocol. Staking takes two forms. You can stake the base asset to become a validator node, or you can delegate your coins to a staking node to earn staking rewards.
You may have noticed the token doesn’t directly have governance capabilities. This is because CVNs handle the governance aspect. CVNs’ integrity during the decision-making process is determined through a trust score. The score takes into consideration its stake and past behaviors.
How do you become a CUDOS Validator Node?
To become a CUDOS Validator Node, a node has to stake 2 million CUDOS tokens (with a minimum 3-month lockup). Fortunately, a validator node receives a percentage of the transaction fees charged on tasks. Also, they receive staking rewards. On the other hand, developers benefit from enhanced security provided by CVNs’ hardware encryption.
CUDOs’ layer 2 network will run up to a maximum of 100 validators, so slots are limited!
Staking on the CUDOS Protocol
CUDOS supports delegated staking. With this scheme, CUDOS token holders stake their tokens with validators who then interact with the protocol. Validators’ stake amount determines the kind of jobs a CVN will receive. For example, the bigger the stake, the larger the jobs, the higher the rewards.
the CUDOS token also acts as a governance token and the stake size is a measure of a validator’s voice in governance matters. If a validator misbehaves, the network confiscates its stake. For instance, if they fake the outcome of a task to save on computational power.
Note that individual validators can decide whether or not to involve delegators when making decisions.
If you wish to un-stake your CUDOS tokens, be aware that the un-bonding period takes a total of 21 days.
Staking rewards on the CUDOS network
CUDOS will pay out staking rewards over a 10 year period. The first and second year reward levels are fixed, and from year 3 onwards the reward levels will be decided by community vote using the governance mechanism.
CUDOS is also giving a ‘lockup rewards multiplier’ when you have staked your tokens for a set period. Currently, they plan to give a 50% bonus after staking for 6 months and a 100% bonus for a 12 month locked stake.
Conclusion
The CUDOS protocol brings a new dimension to the possibilities of blockchain technology. By being Turing complete, the protocol can handle many tasks from different blockchains regardless of their programming language. Another noble approach is the use of data centers and allowing everyone from desktop PC users to mobile device users to lease their idle computing power.
Its base asset gives holders incentives to either delegate their coins or actively handle tasks on the network. With the current rise in DeFi and blockchain adoption, CUDOS opens the door wider to the world of unlimited possibilities.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.

